Model Constrained Bayesian Neural Networks for Uncertainty Quantification
Major Activities
Model-constrained deep neural networks are capable of learning from both training data and the mathematical models governing a phenomenon of interest; these methods have direct applicability to inverse problems. In this project we extend model-constrained deep neural networks to a model-constrained Bayesian neural network (MCBNN) form, facilitating the solution of inverse problems while simultaneously quantifying uncertainty in predictions. We produce MCBNN forms for a single network learning the inverse map, as well as autoencoders learning both the forward and inverse maps simultaneously. Furthermore, novel training methods for MCBNN allow us to sidestep the common Bayesian issue of defining a prior for the Bayesian neural network parameters.
Significant Results
We are testing MCBNN by solving three inverse problems governed by Poisson’s equation, Burger’s equation, and the Navier-Stokes equations’, respectively. The following figure shows some basic qualitative results for MCBNN on a test sample after solving the Poisson inversion, illustrating the uncertainty quantification capability of MCBNN.
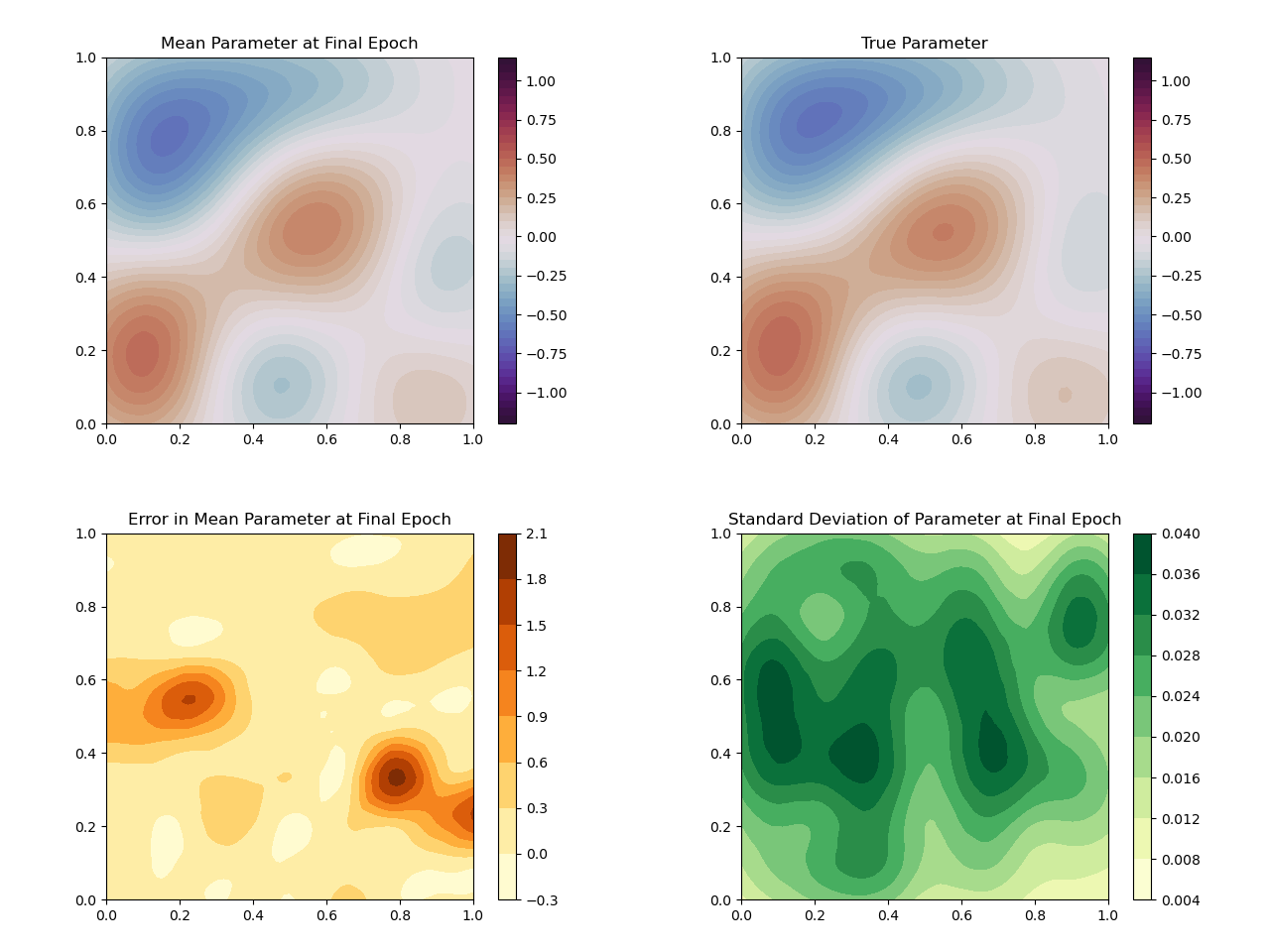
Simulation for Burger’s equation and the Navier-Stokes equations is underway. Lastly, a Tikhonov neural network form of MCBNN is also being tested.