Model-constrained Gaussian processes for physics- and dimension-reduction of PDEs
We developed an approach which uses model-constrained Gaussian process methods to compute quantities of interest (QoIs) of 2D/3D high fidelity (HF) nonlinear problems using only sparse HF data and low dimensional or simplified simulations/approximations for {unseen parameters}. In general, our method is compatible with nonlinear equations and any QoI functional that is linear on the low fidelity (LF), although it is extensible to nonlinear QoIs as well.
Major Activities
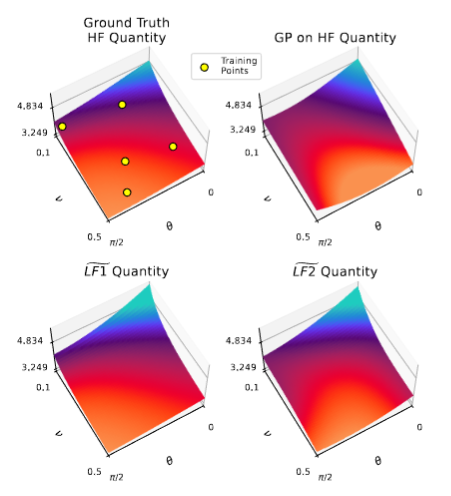
We consider standard Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) on the HF QoI itself as a baseline. Our method is instead inverting for a correction to a LF partial differential equation (PDE) using Gaussian Process methods then learning a correction. Numerically we have validated our approach using 3D advection-diffusion as HF, 2D Poisson (LF1) and 1D advection-diffusion (LF2) as options for low-fidelity. When modeling the state average QoI and varying advection direction \(\theta\) and viscous strength \(\nu\), our method outperforms the baseline.
Significant Results
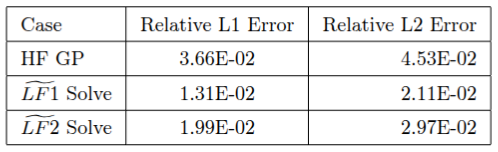
Here the accented \(\widetilde{LF1}\), \(\widetilde{LF2}\) refer to the corrected models corresponding to LF1 and LF2 respectively. The 3D advection diffusion HF and QoI predictions from the baseline (GPR on HF) and our method is shown in the first figure. The corresponding errors across a range of advection direction \(\theta\) and viscous strength \(\nu\) are presented in the table showing the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
QoI result comparison:
QoI error comparison:
HF solution example: