A Model-Constrained Discontinuous Galerkin Network (DGNet) for Compressible Euler Equations with Out-Of-Distribution Generalization
Paper publication
Publication Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045782525001847
Citation:
@article{van2025model,
title={A model-constrained discontinuous Galerkin Network (DGNet) for compressible Euler equations with out-of-distribution generalization},
author={Van Nguyen, Hai and Chen, Jau-Uei and Bui-Thanh, Tan},
journal={Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering},
volume={440},
pages={117912},
year={2025},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
Methodology
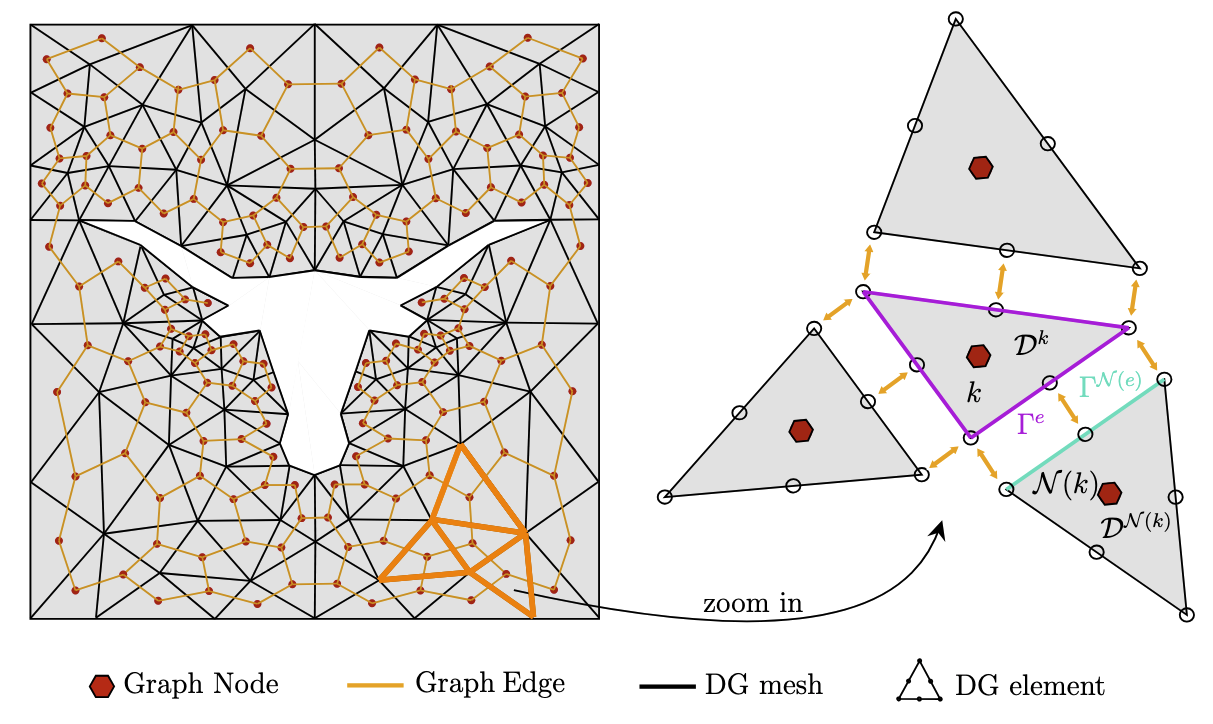
In this work, we developed a machine learning framework to solve shock-type PDEs, in particular, Compressible Euler equations. The core idea is motivated by the dual mesh between Discontinuous Galerkin (DG) method and Graph Neural Network (GNN).
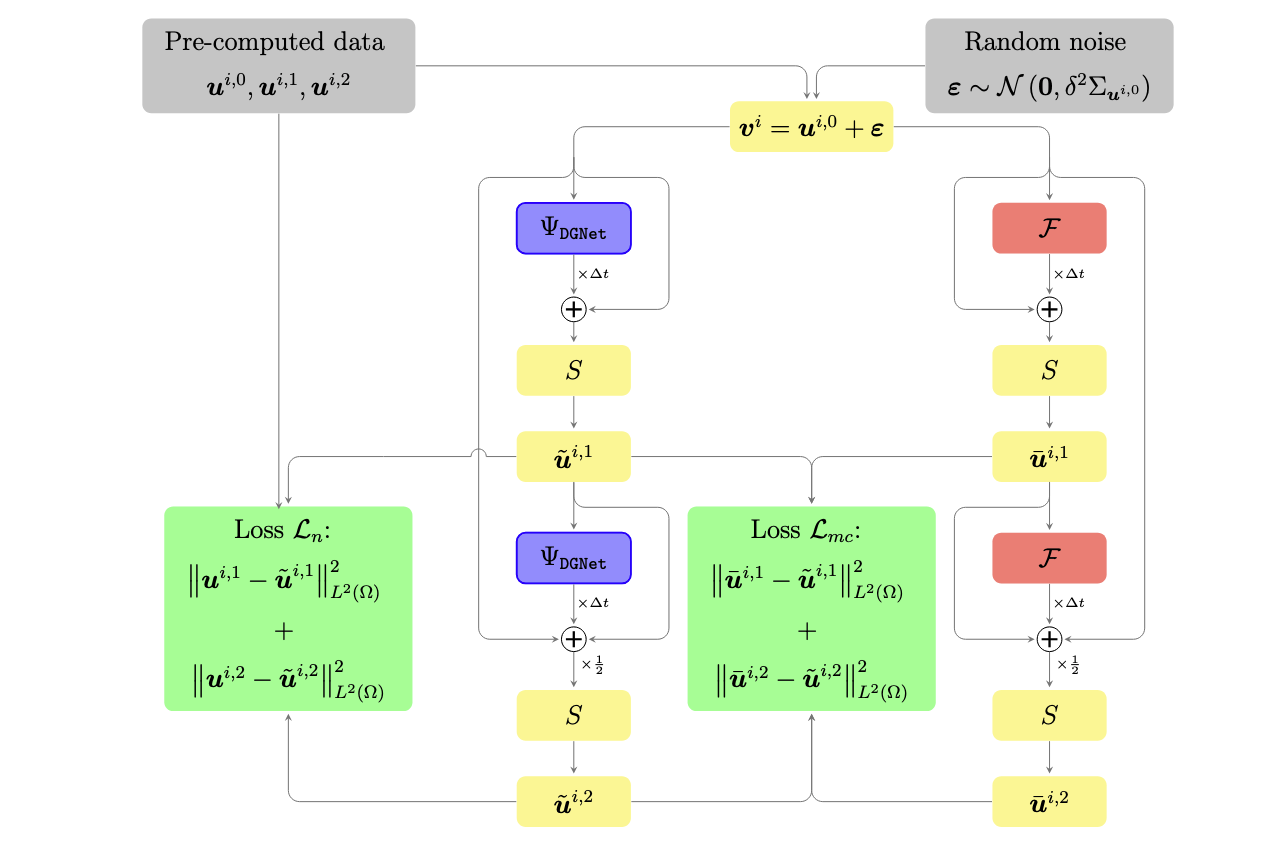
The training data flow is presented as shown in Figure 2. We integrate the data randomization and differentiable solvers to enhance the generalization of neural surrogate models.
Numerical results
- We work on 2D Euler equations
where \(E\) is the total energy per unit volume:
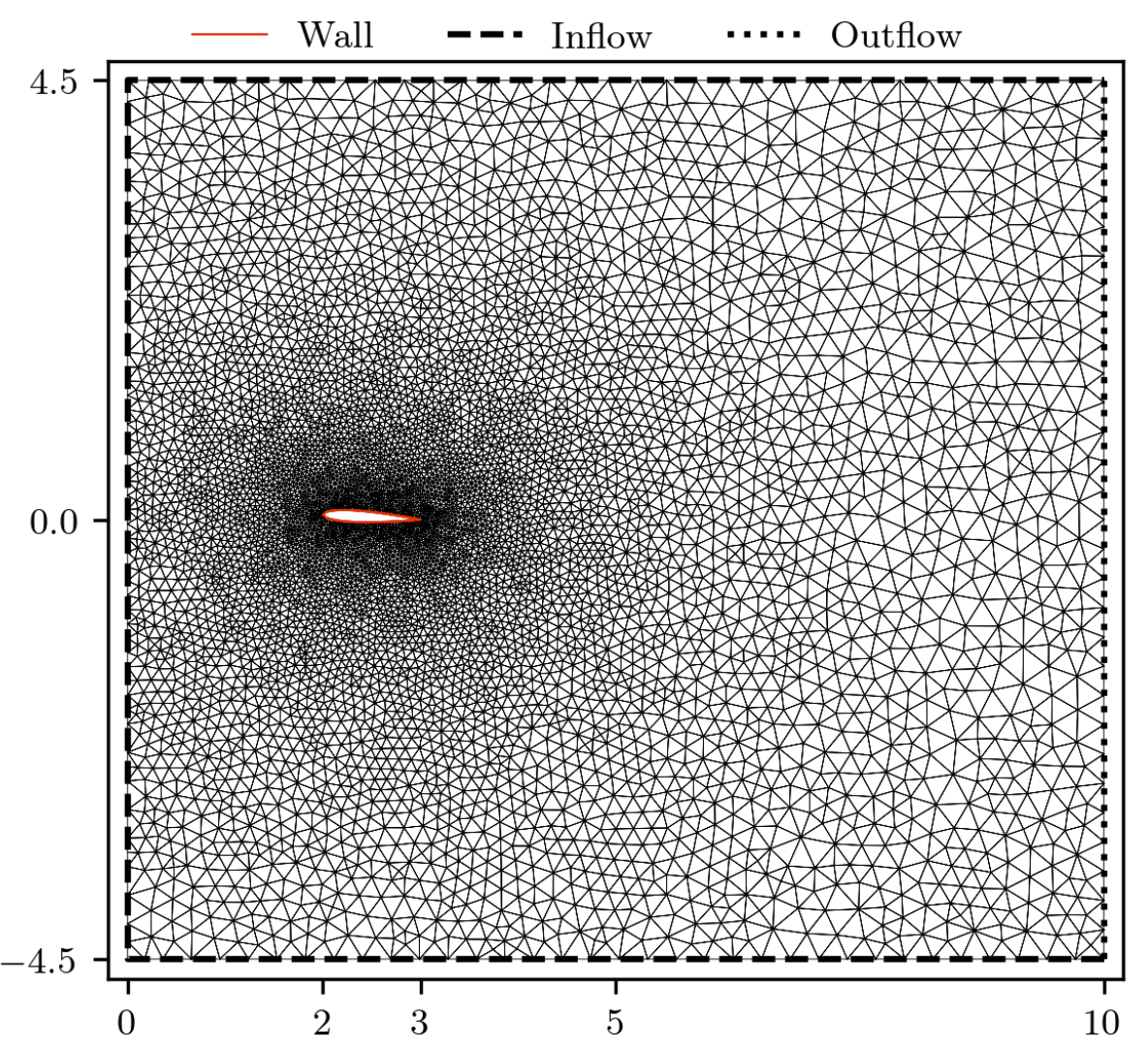
\[E = \frac{p}{\gamma - 1} + \frac{\rho}{2}(u^2 + v^2)\]Problem 1. Airfoil NACA0012
- Training data is generated from Airfoil AoA = 3 and Mach = 0.8, in time interval [0,1.2]s
- Test data is generated from Airfoil AoA = 3 and Mach = 0.8 and Airfoil AoA = 5 and Mach = 1.2 for time interval [0, 7.5]s
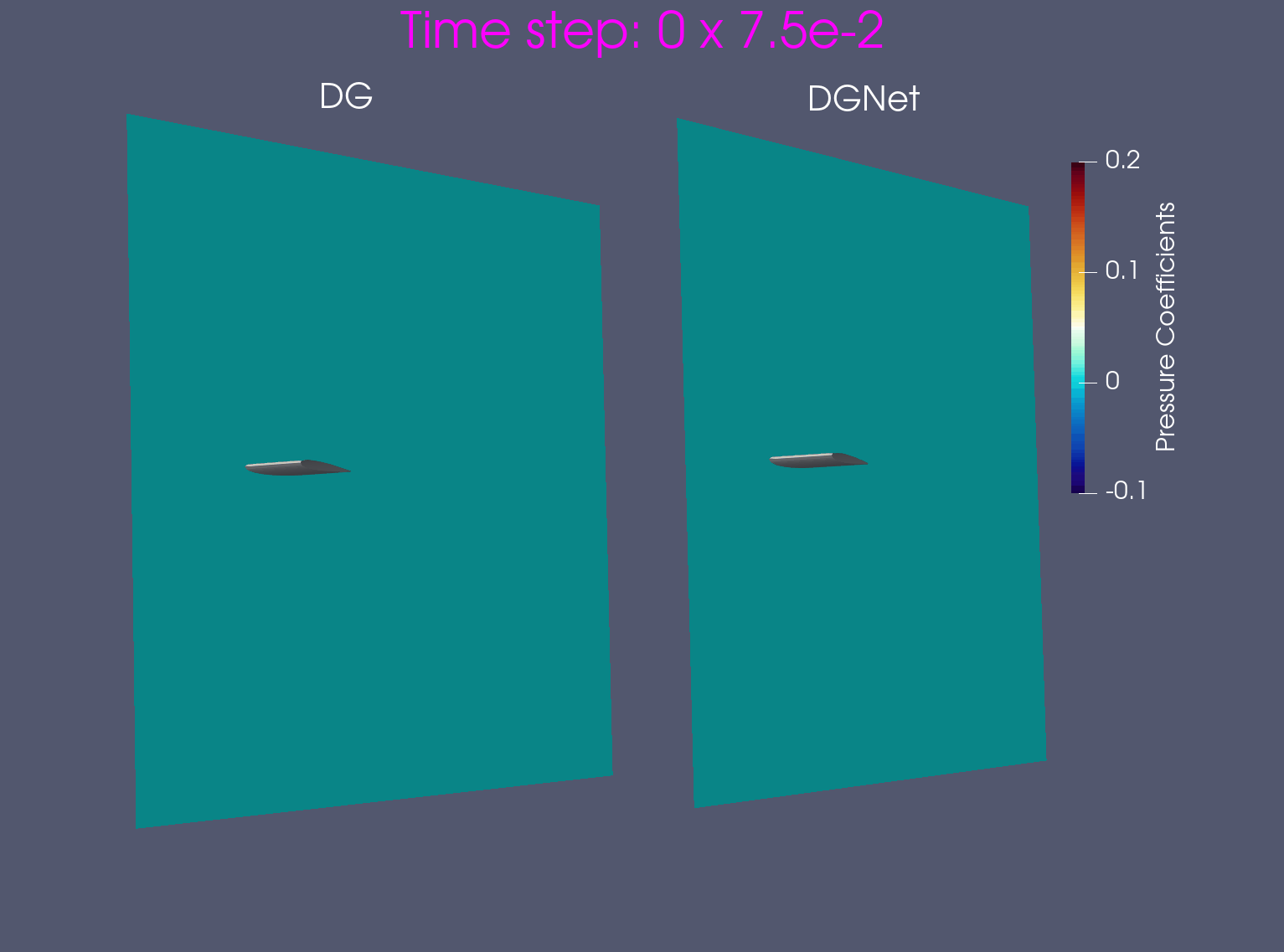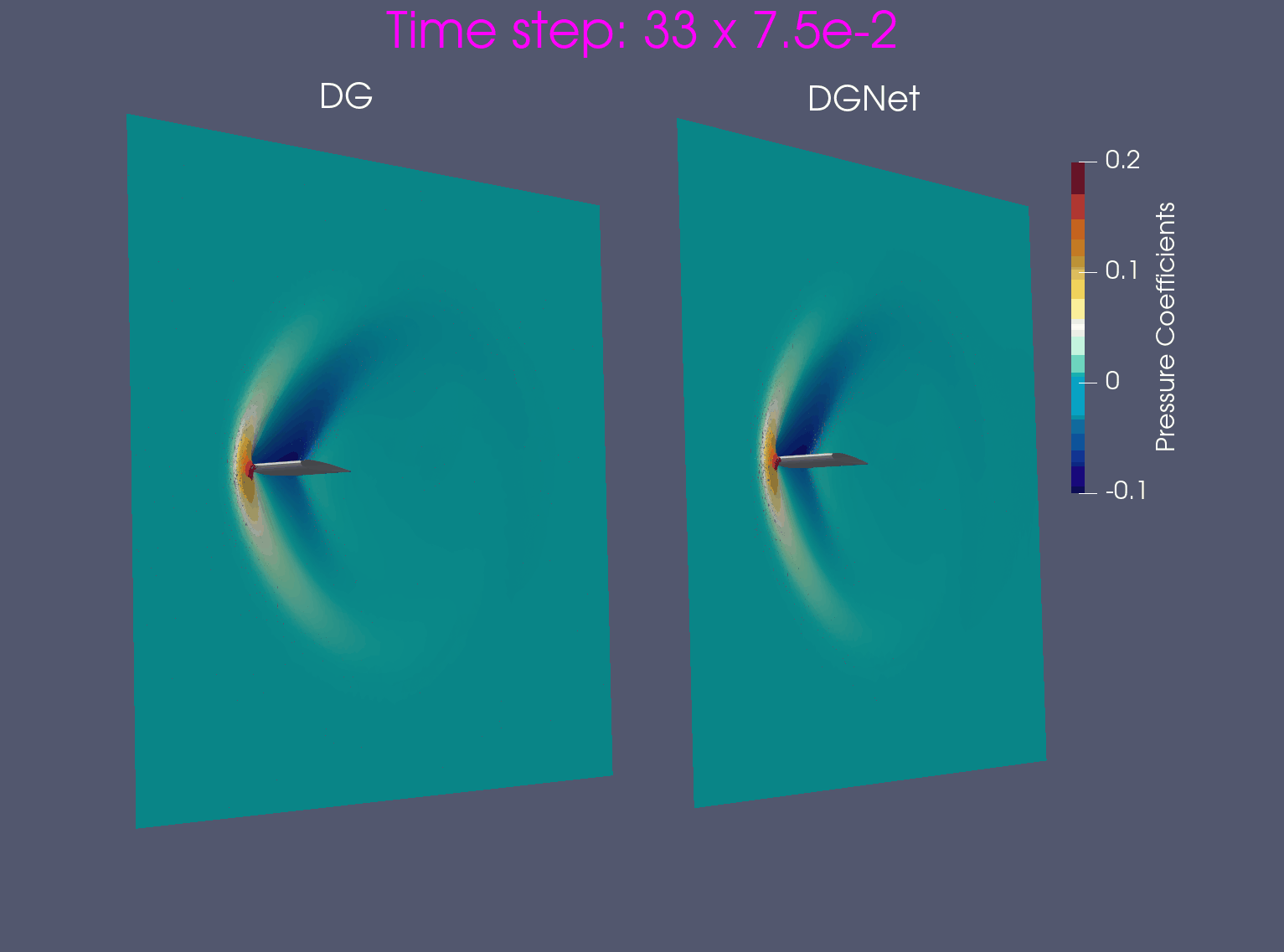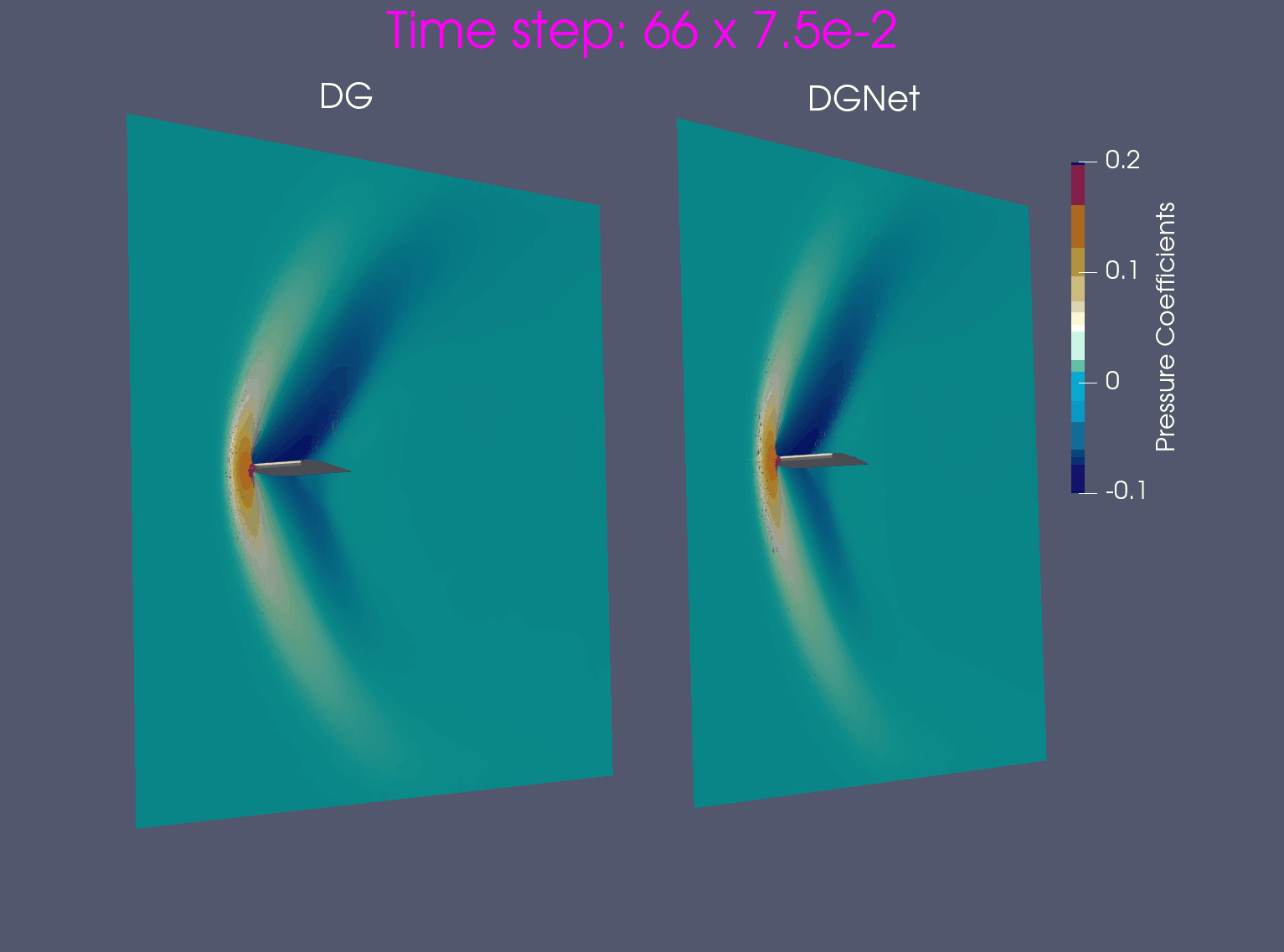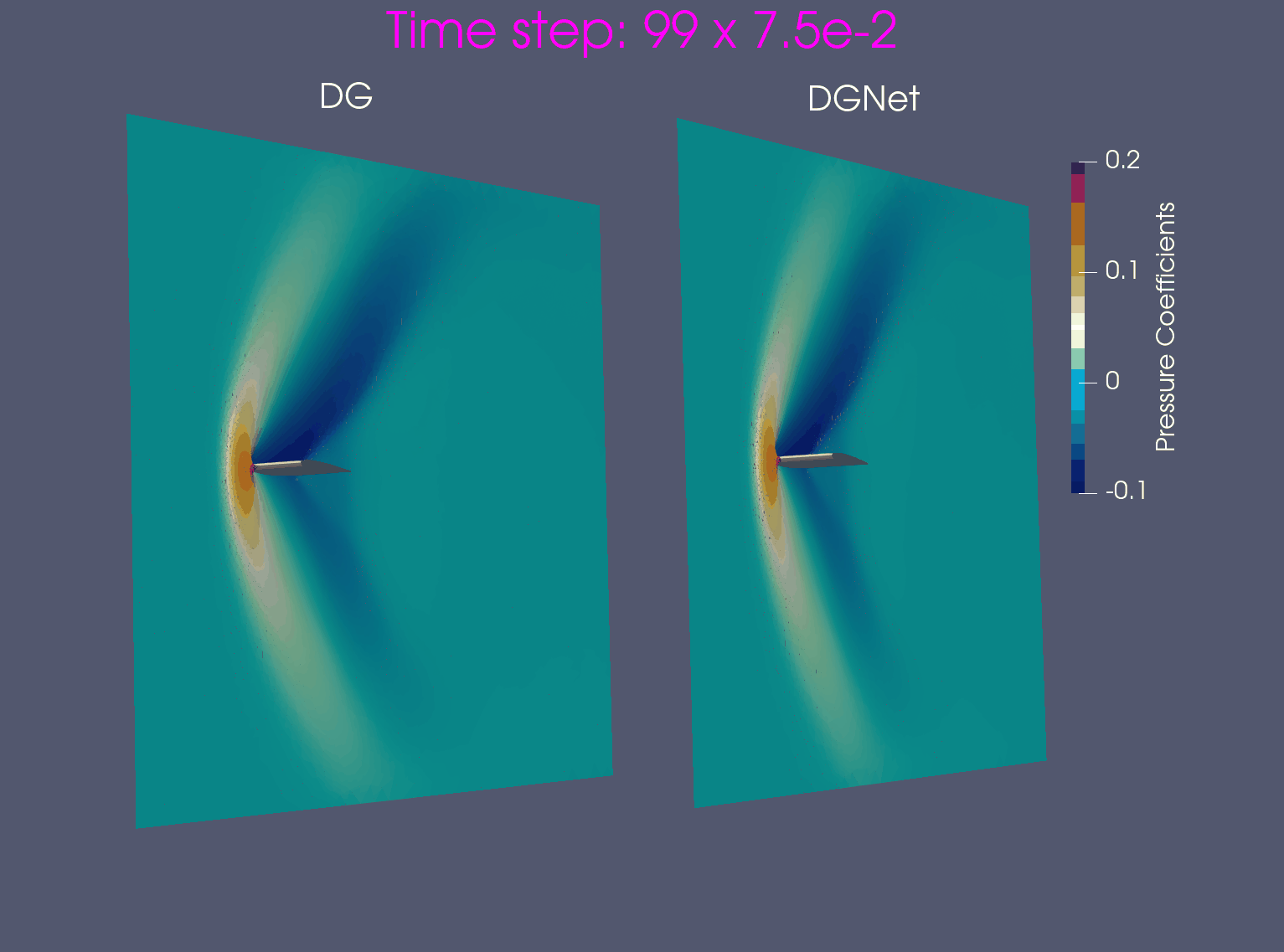
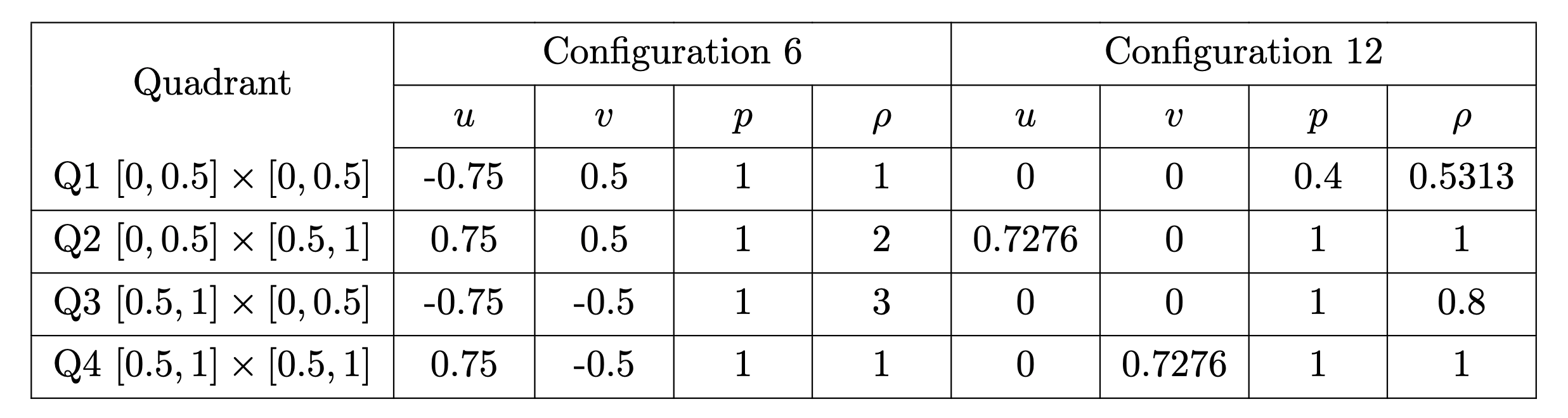
Problem 2. Euler configurations 6 & 12
- Training data is generated from Euler configuration 6 with time interval [0,0.16]s
- Test data is generated from Euler configuration 6 for time interval [0, 0.8]s and Euler configuration 12 for time interval [0, 0.25]s

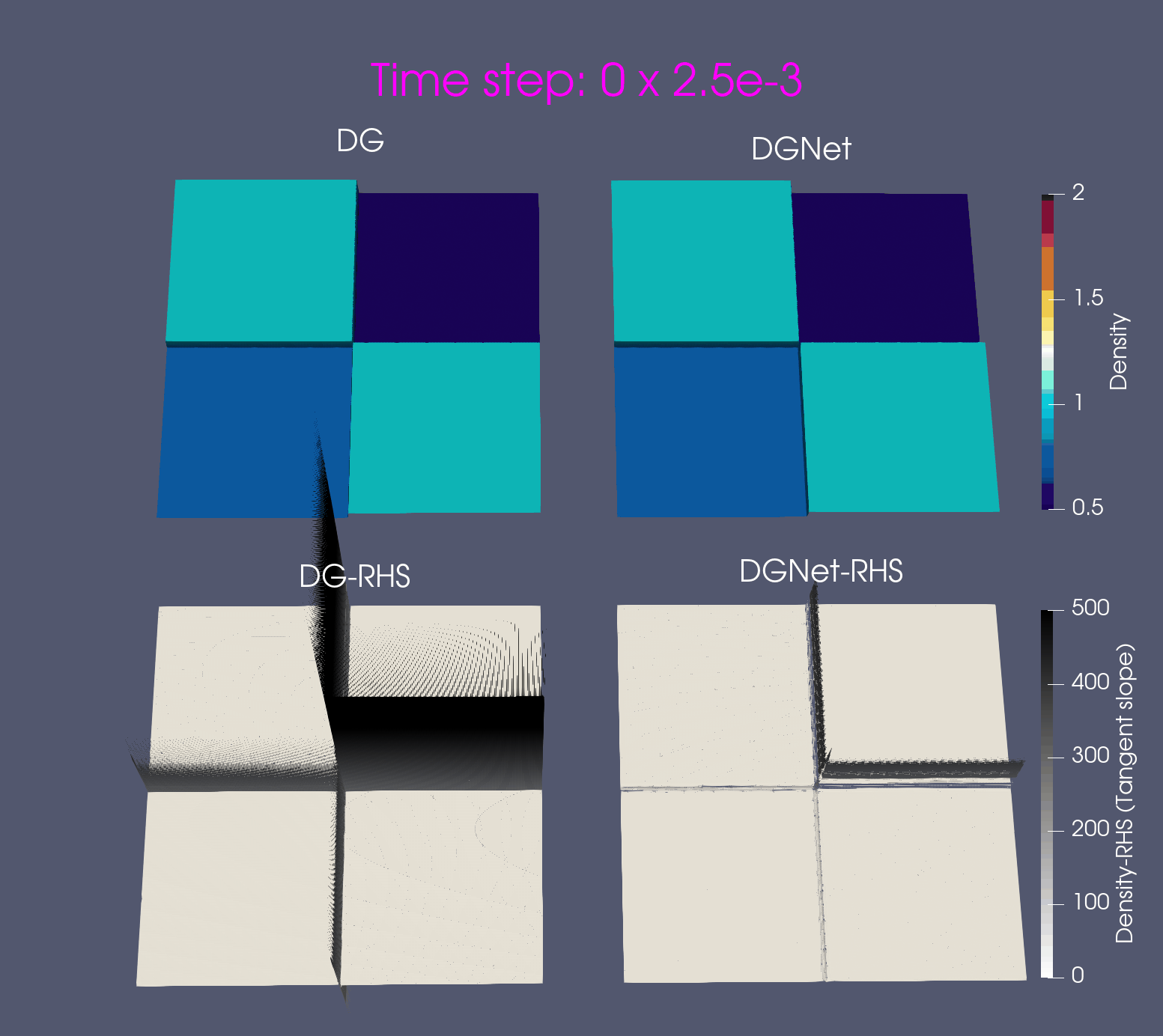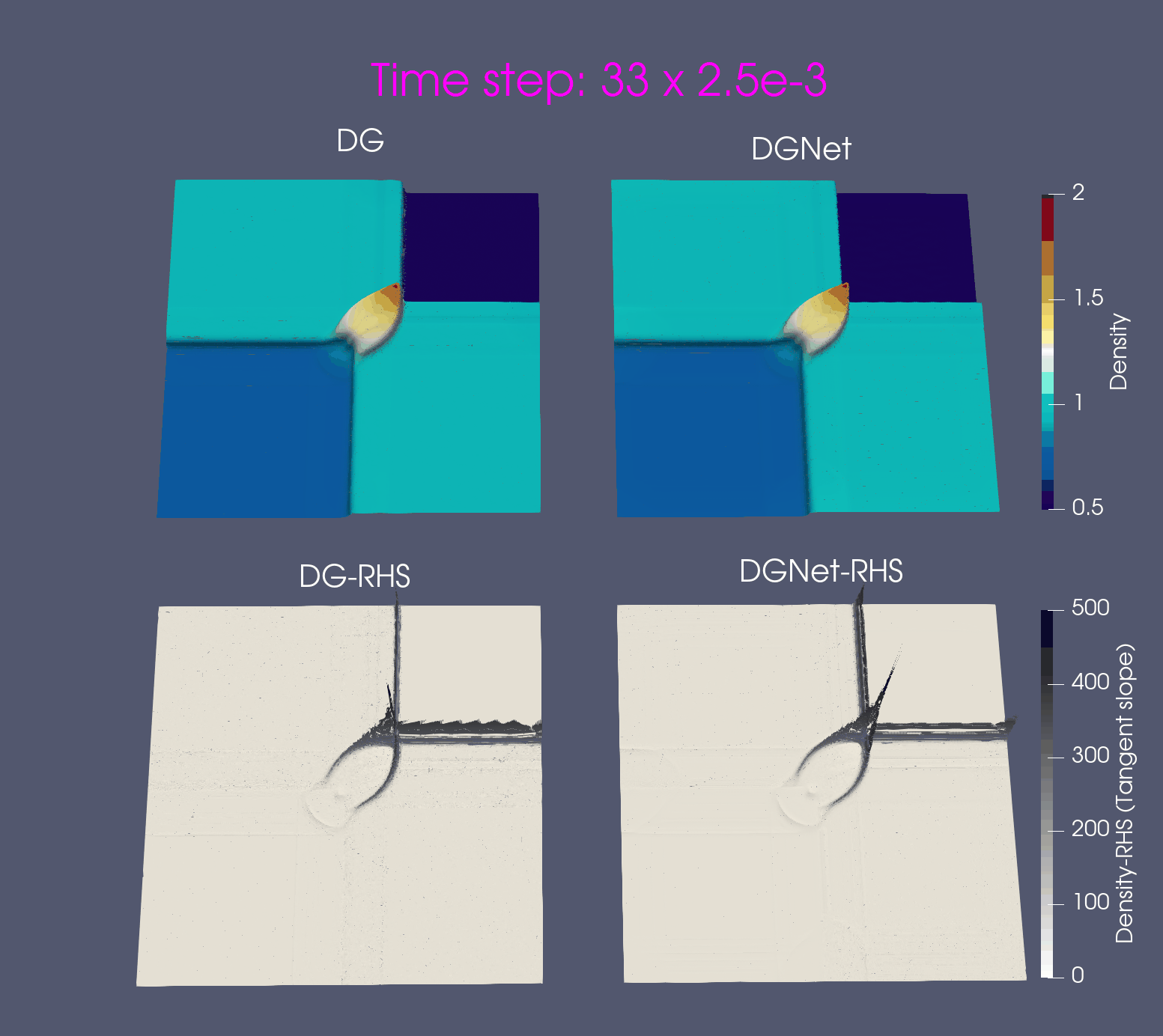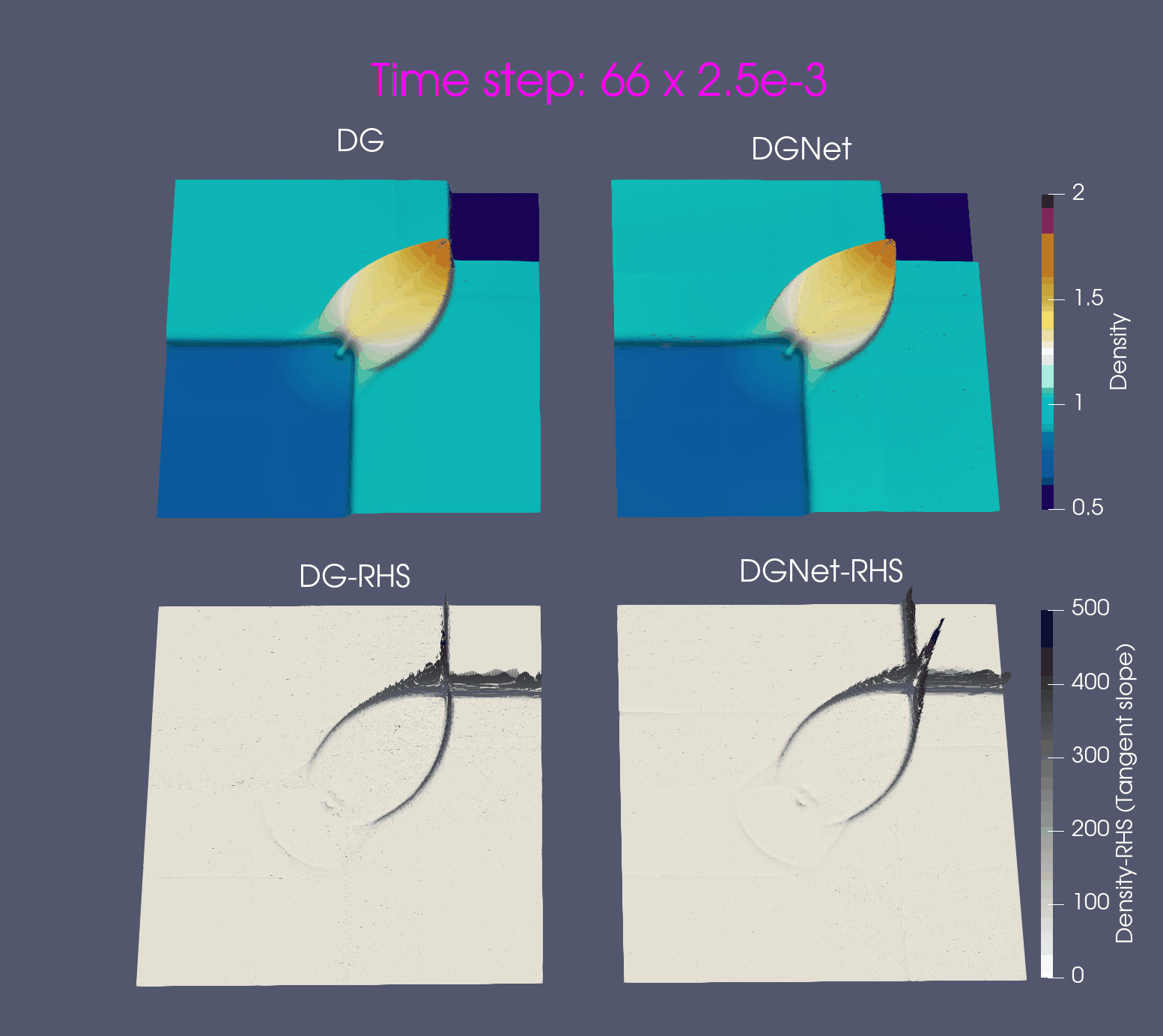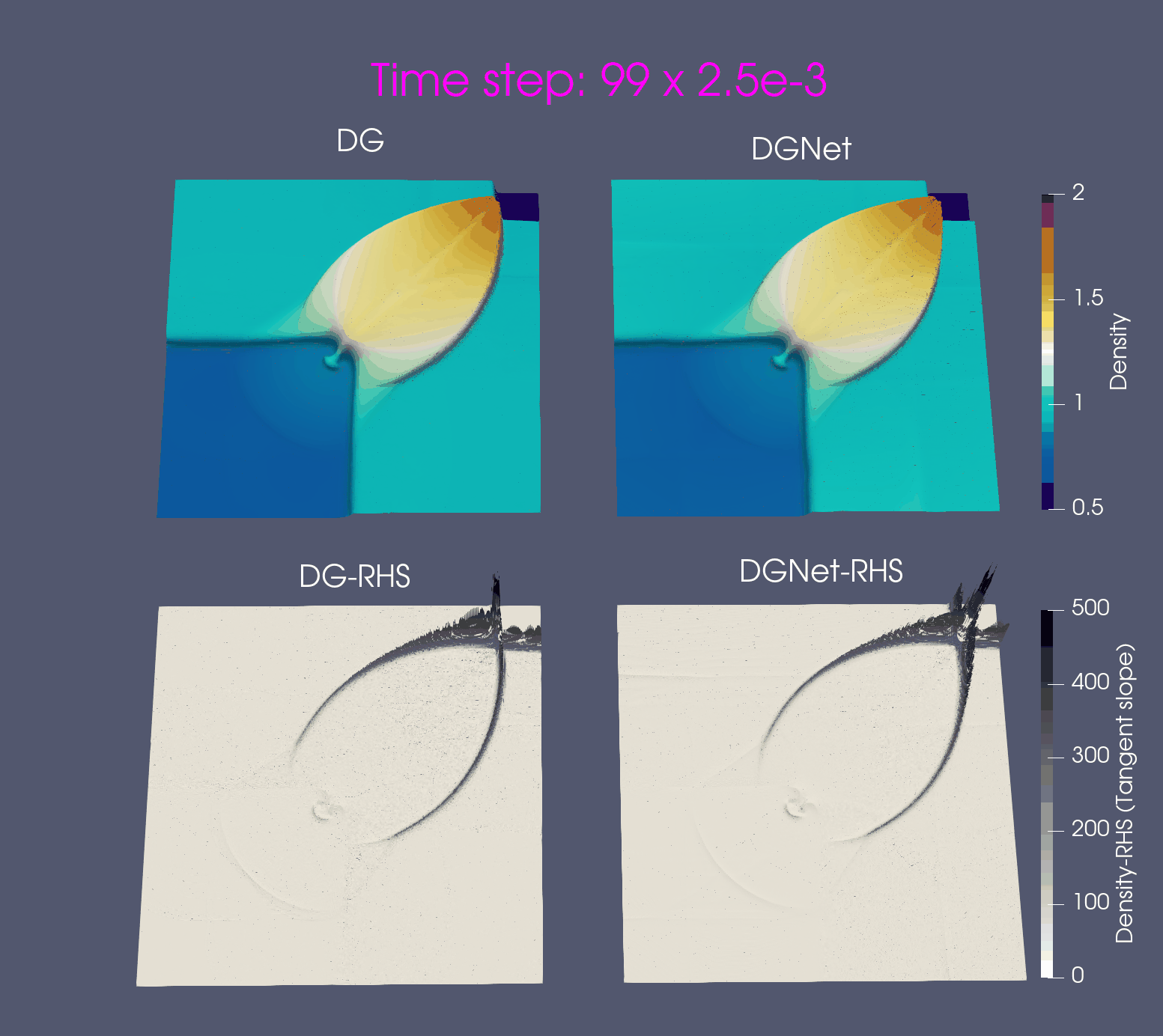
Problem 3: Double Mach Reflection
- Training data is generated with time interval [0,0.02]s
- Test data is generated with time interval [0, 0.25]s
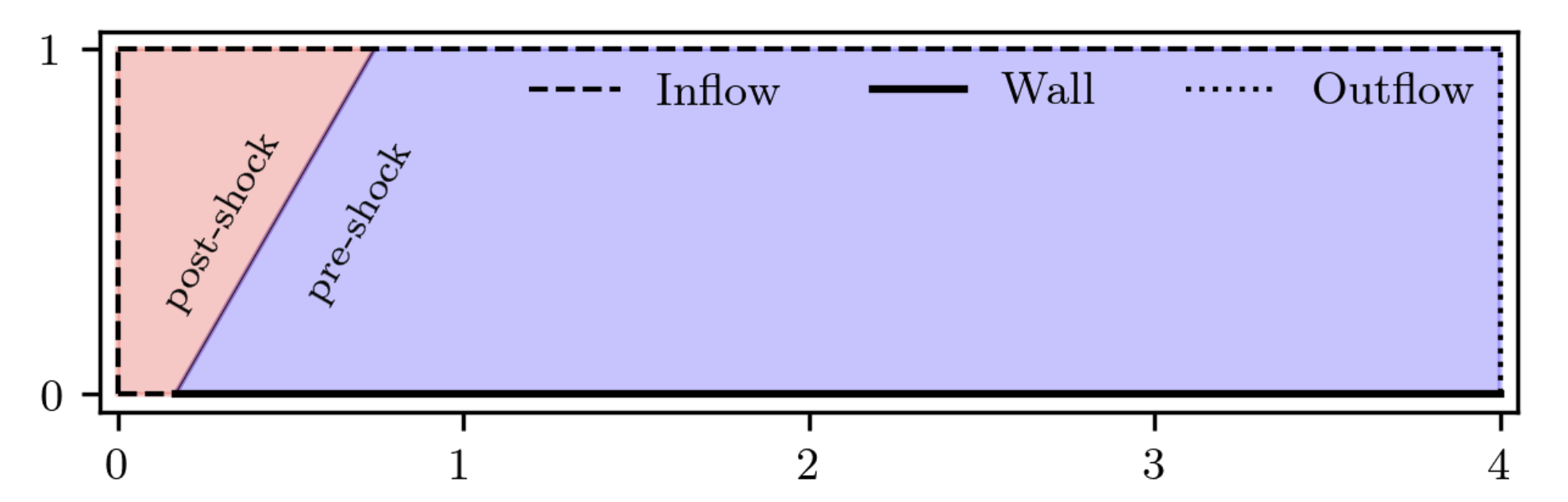
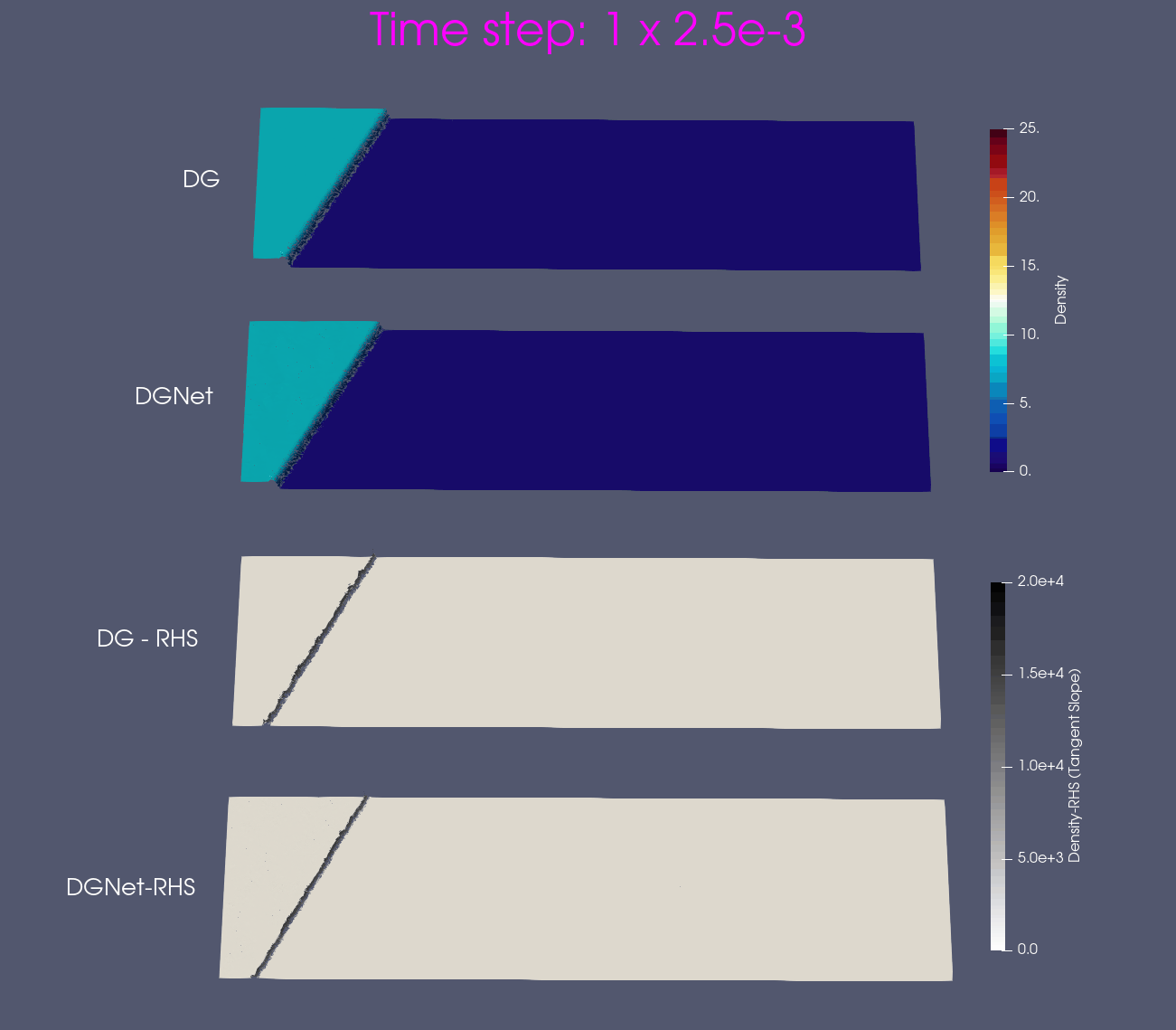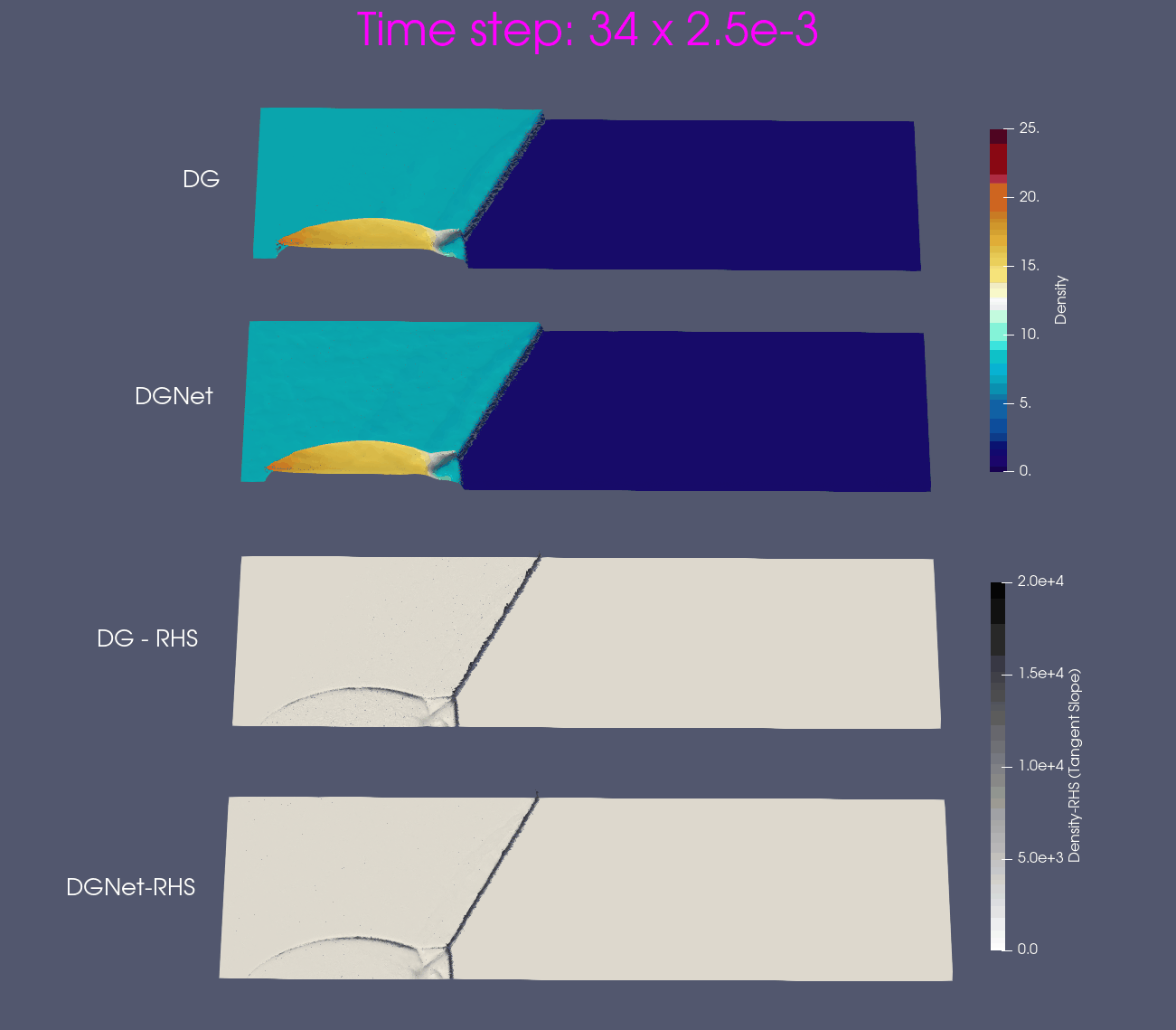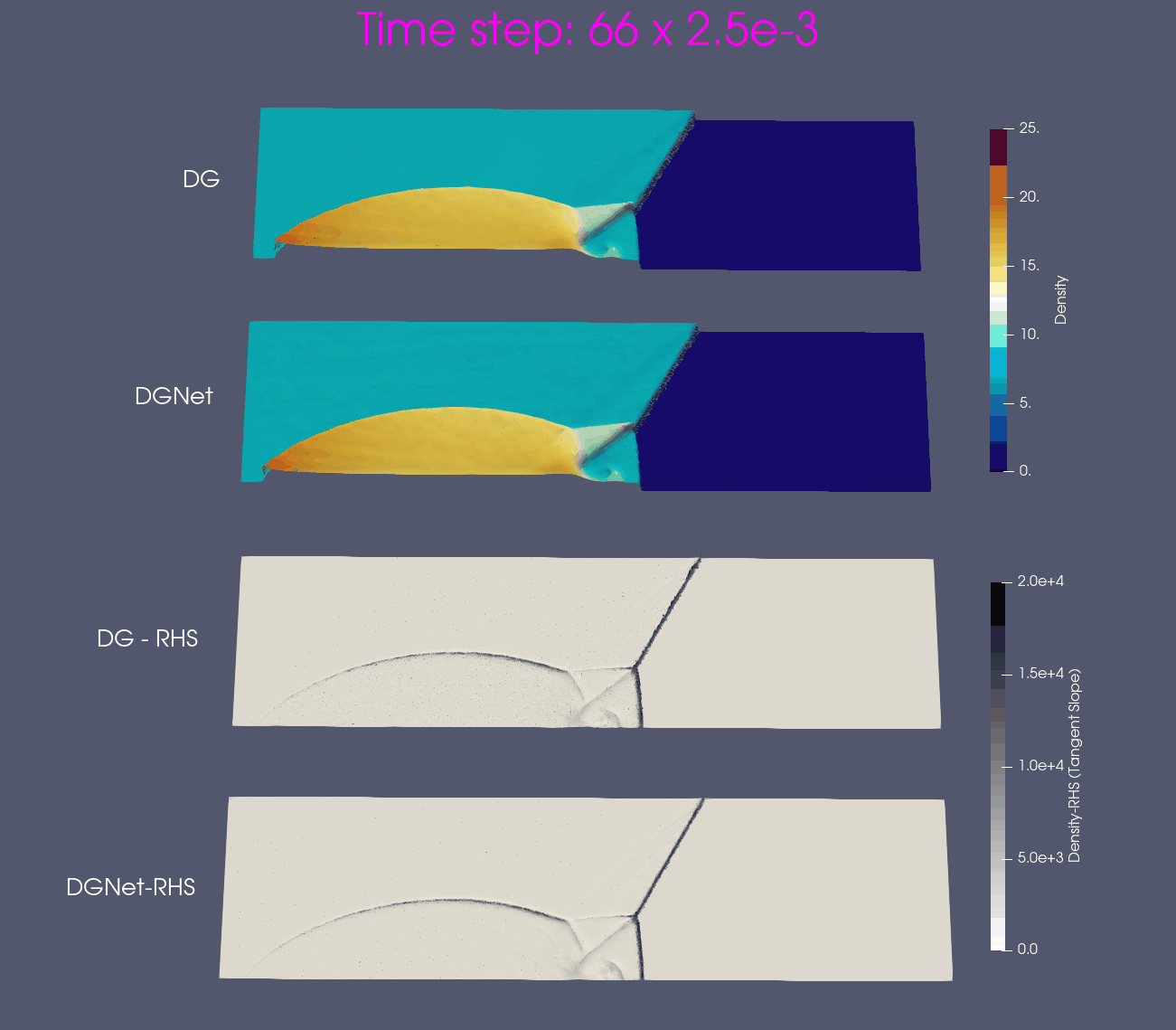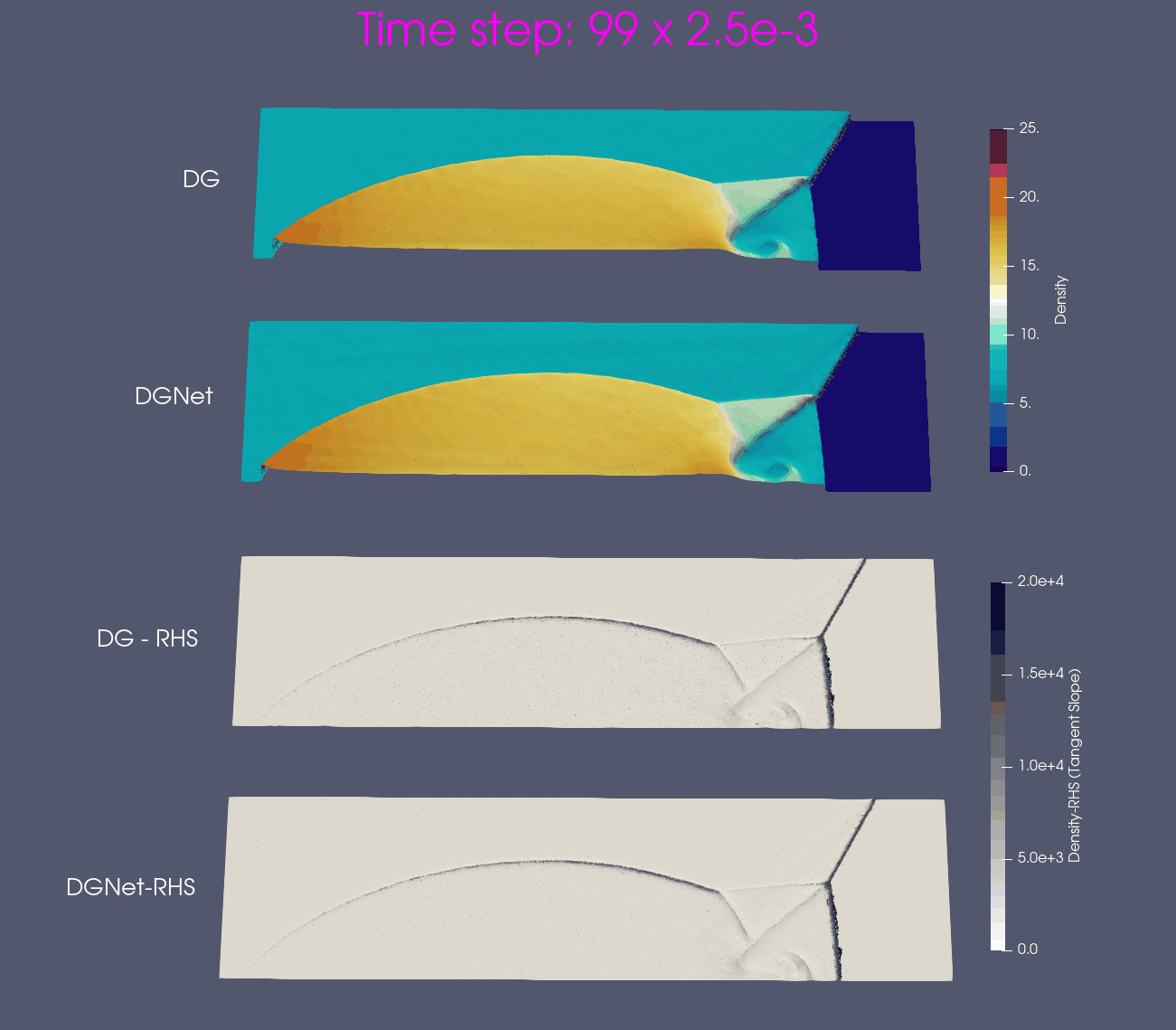
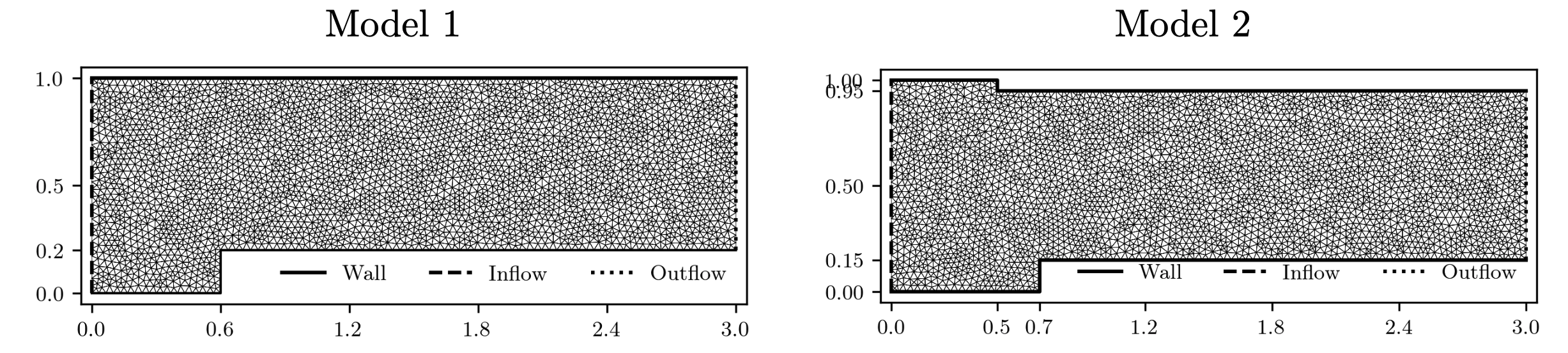
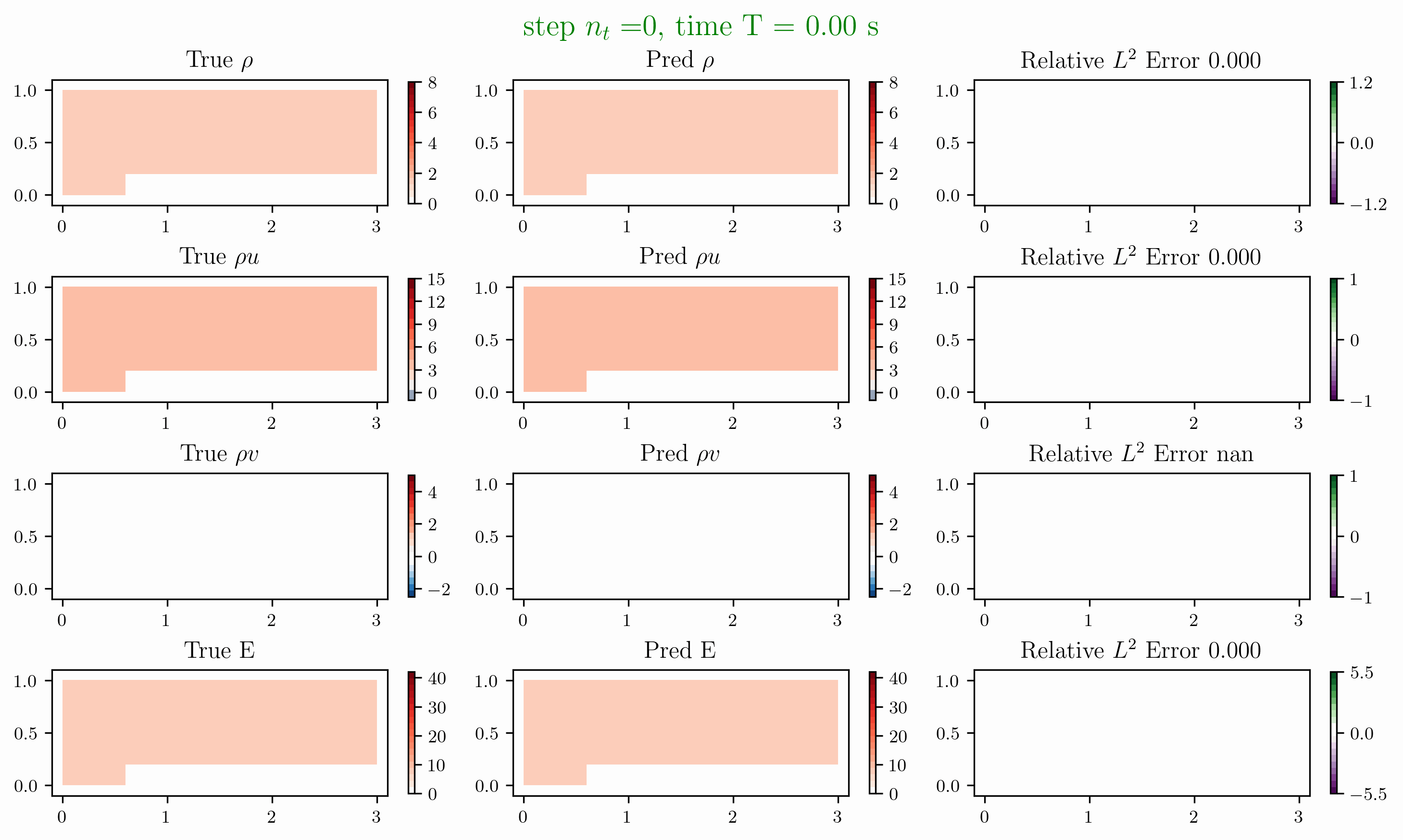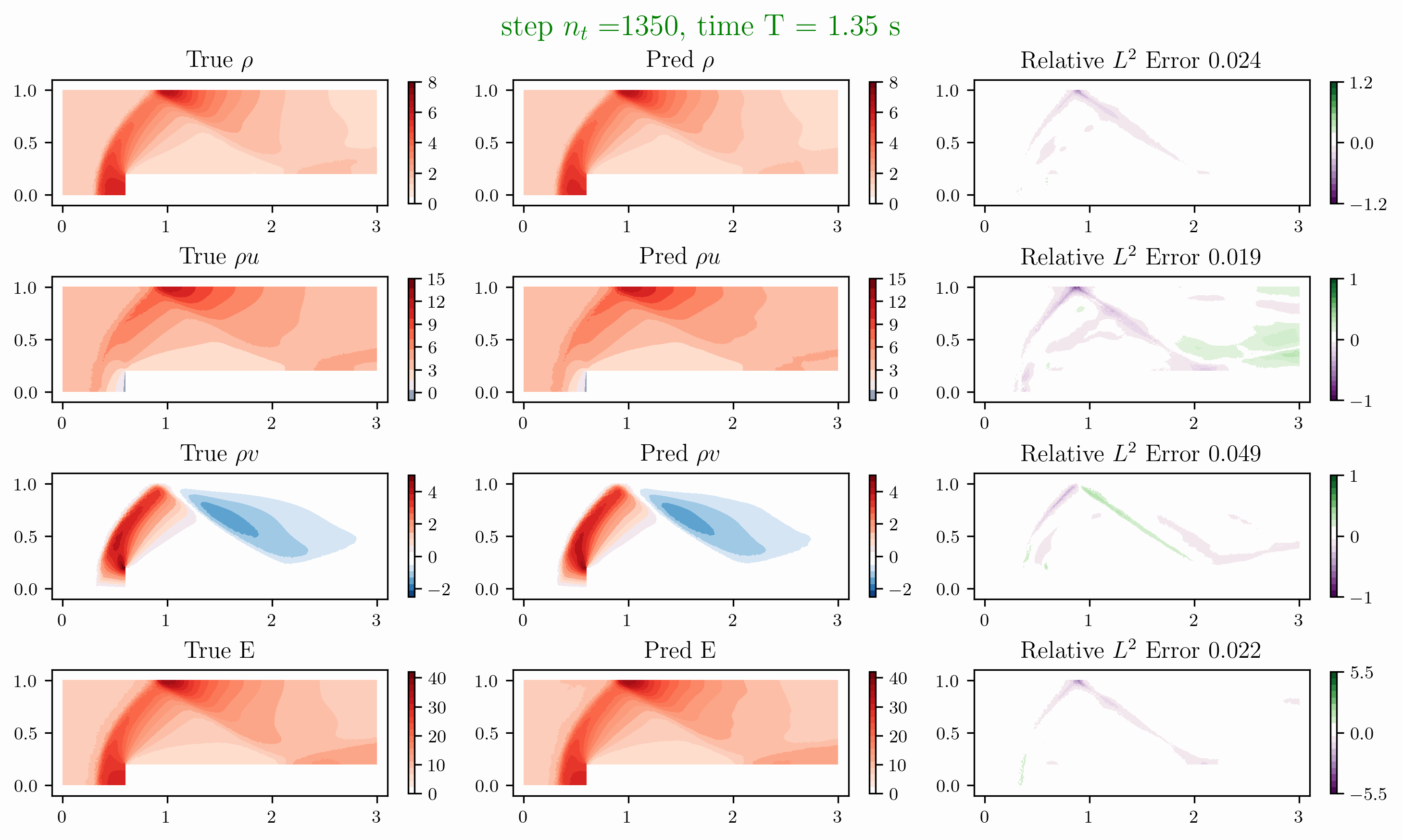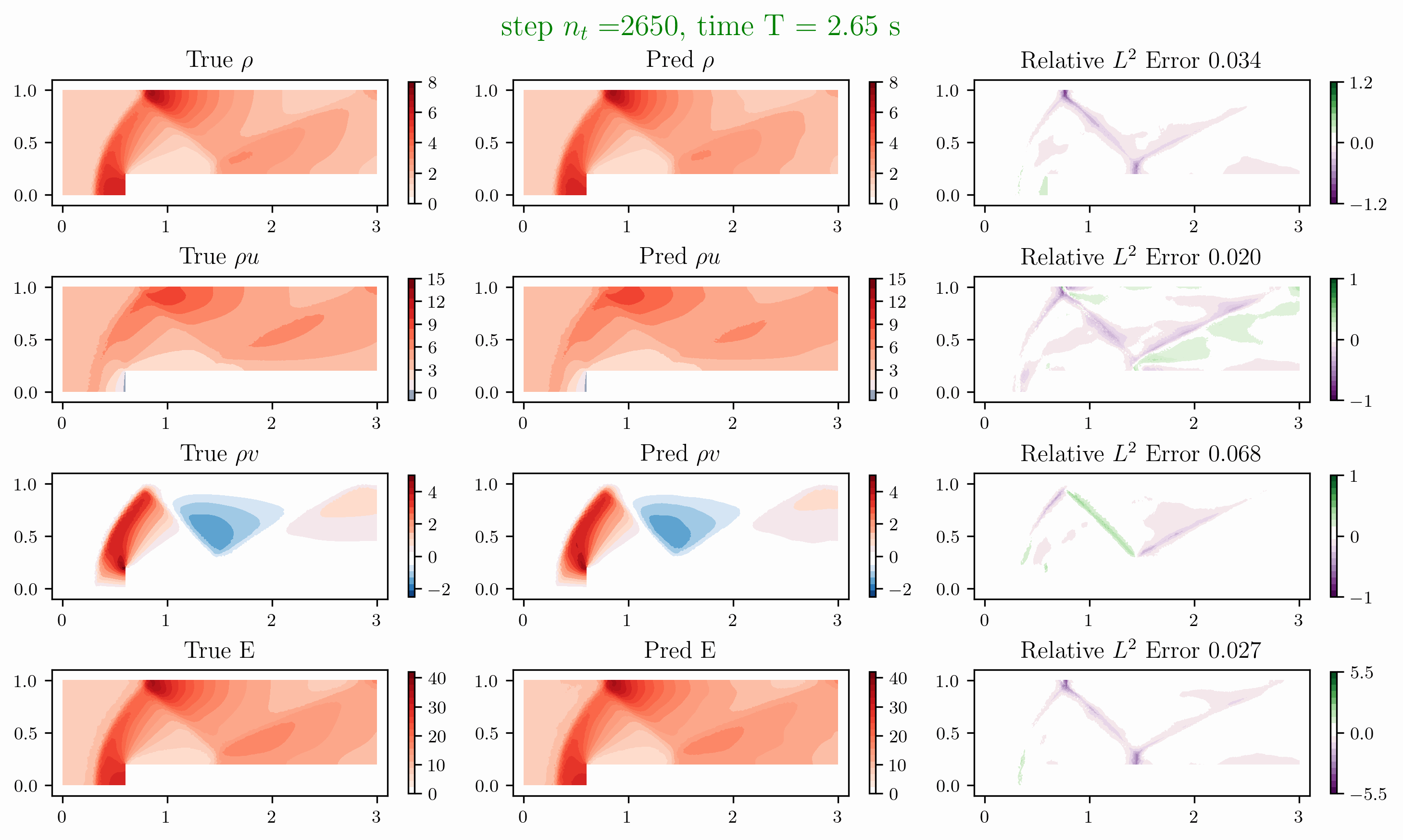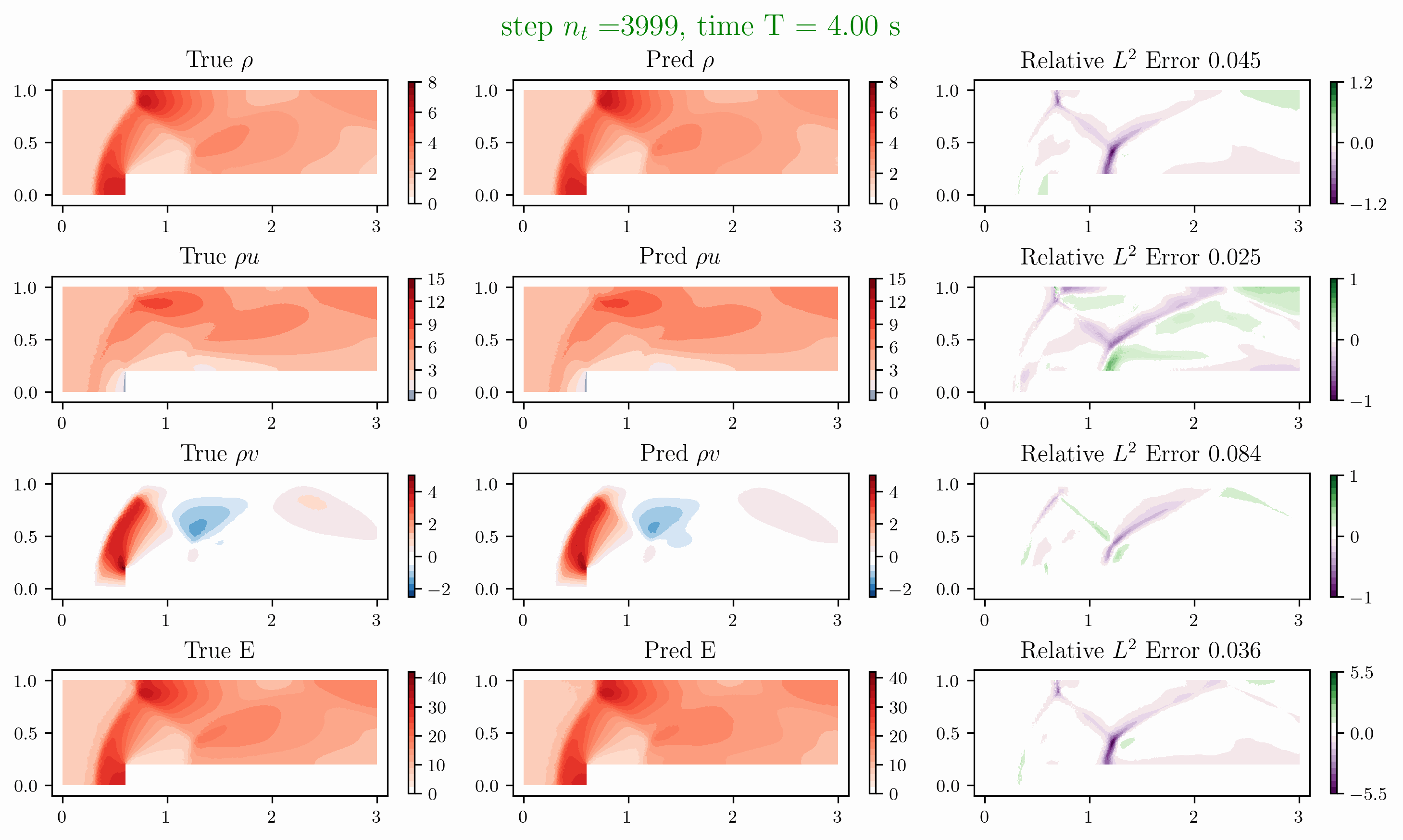
Problem 4. Forward facing corner
- Training data is generated from Model 1 with time interval [0,1]s
- Test data is generated from Model 1 and Model 2 for time interval [0,4]s
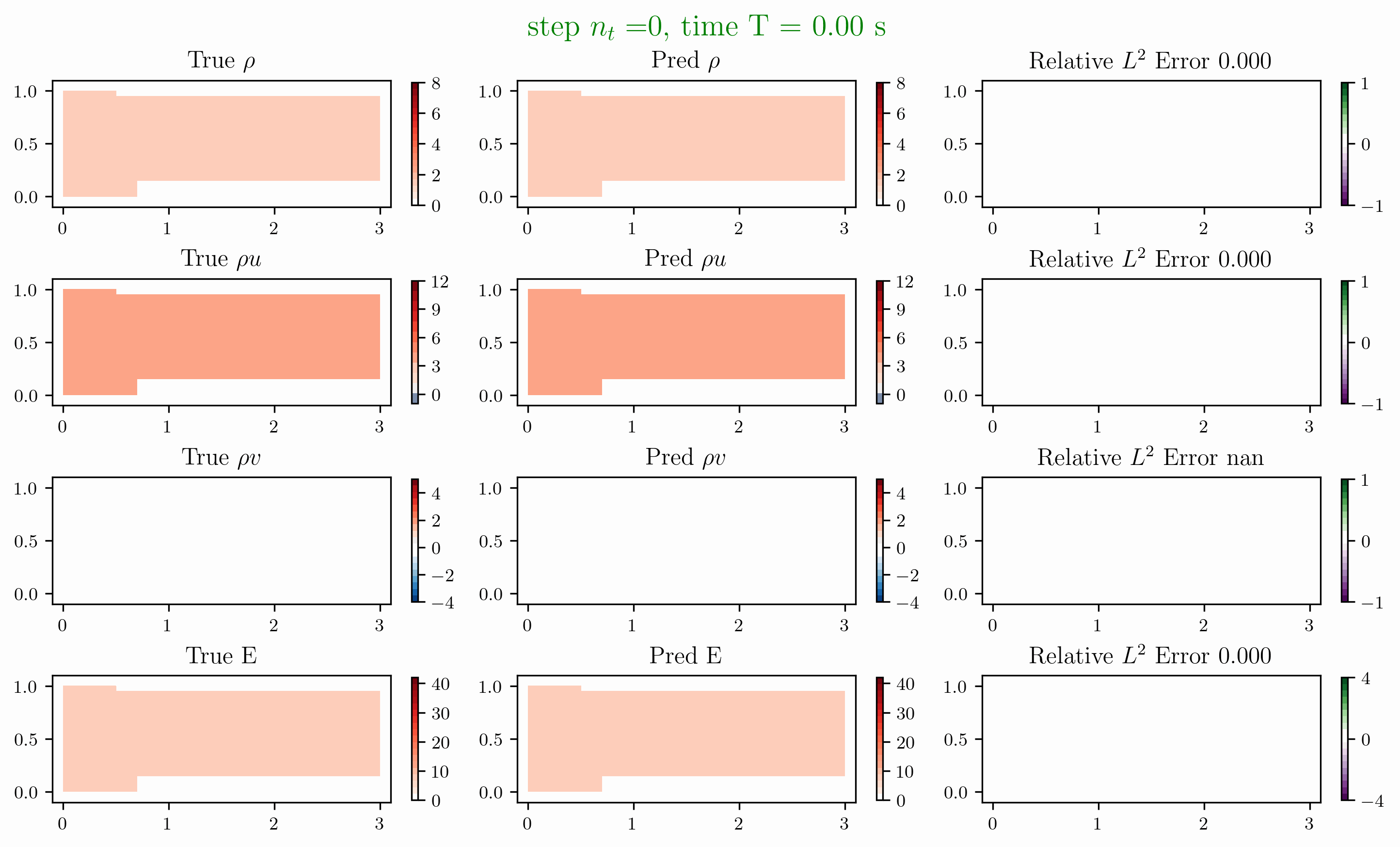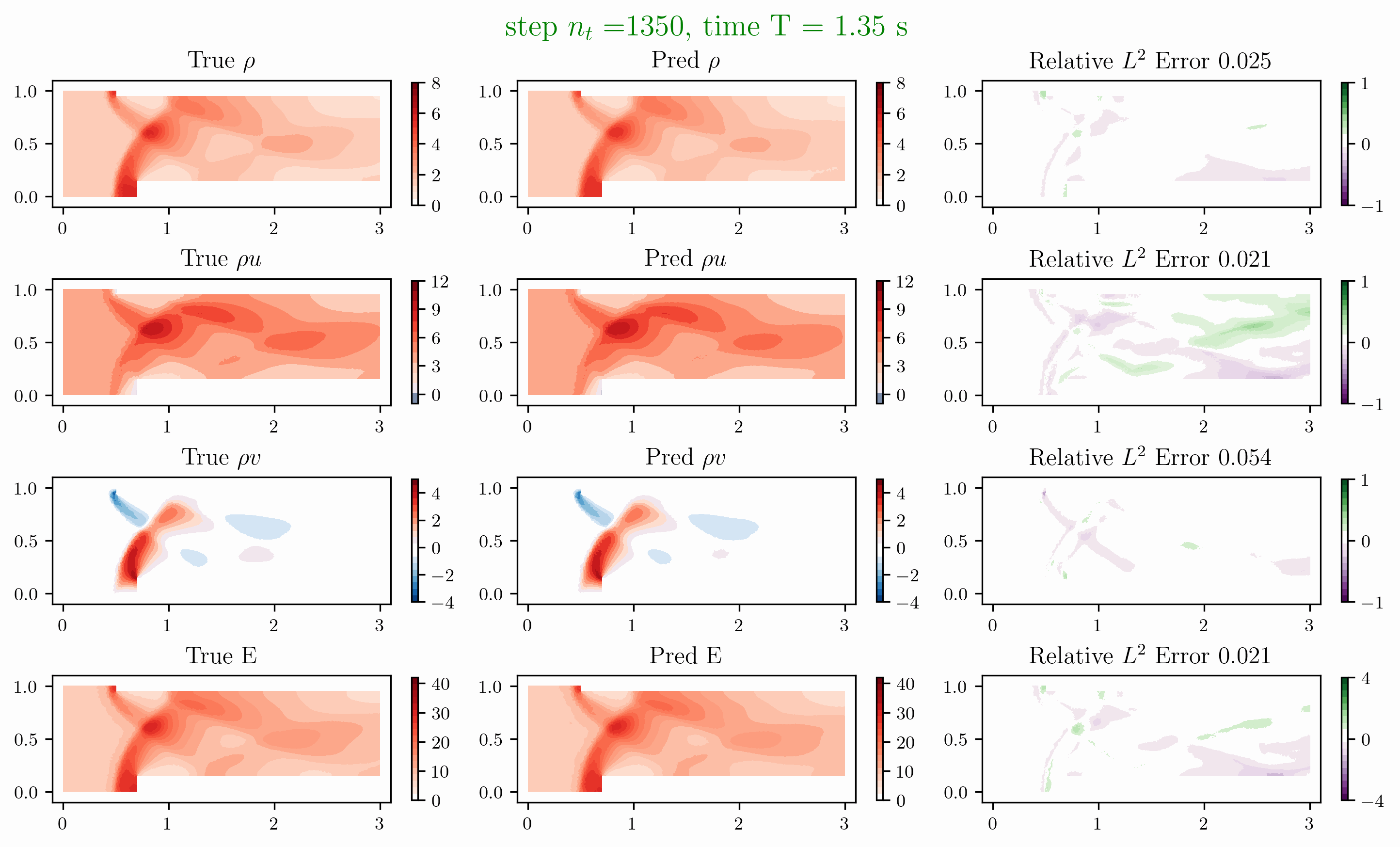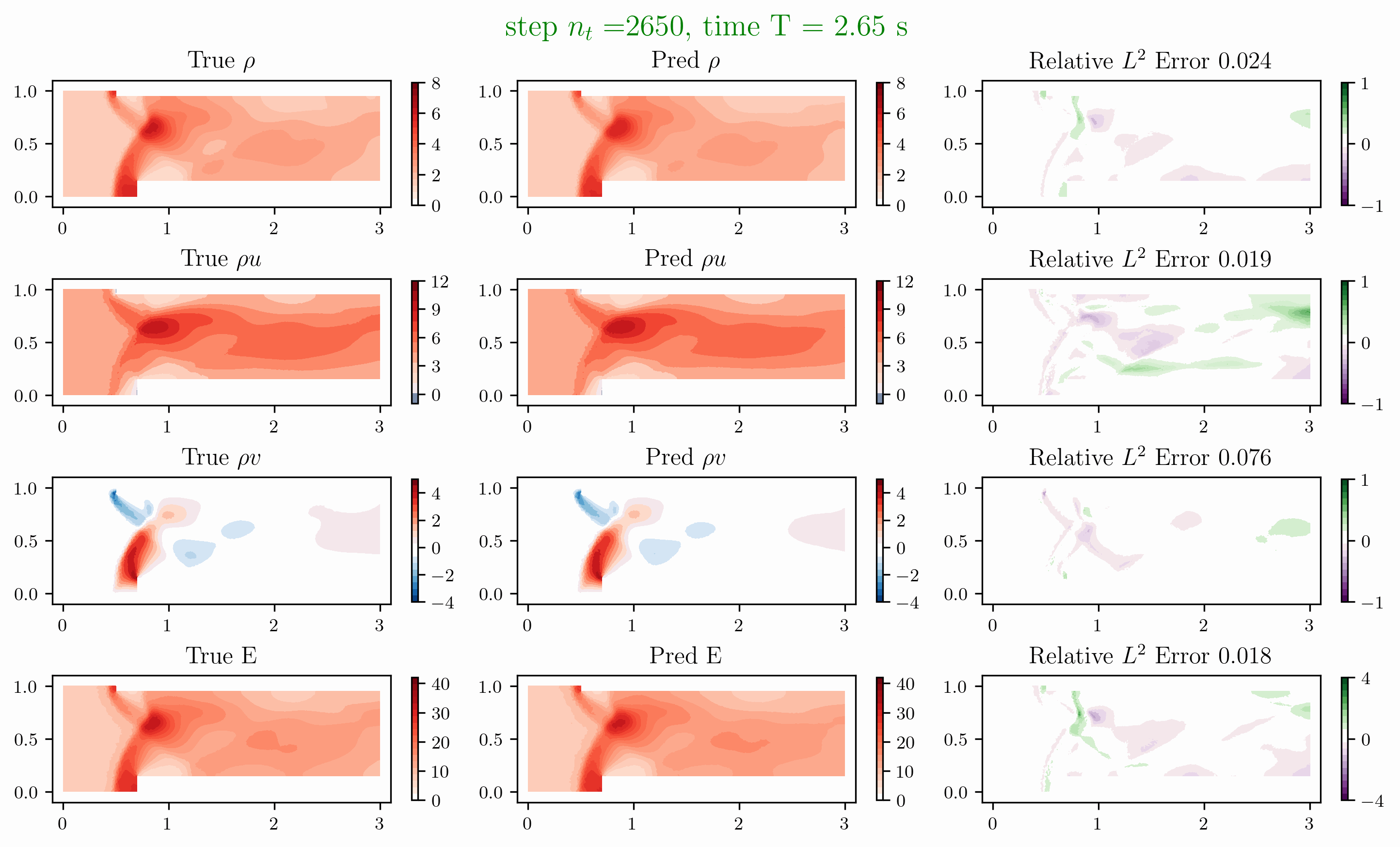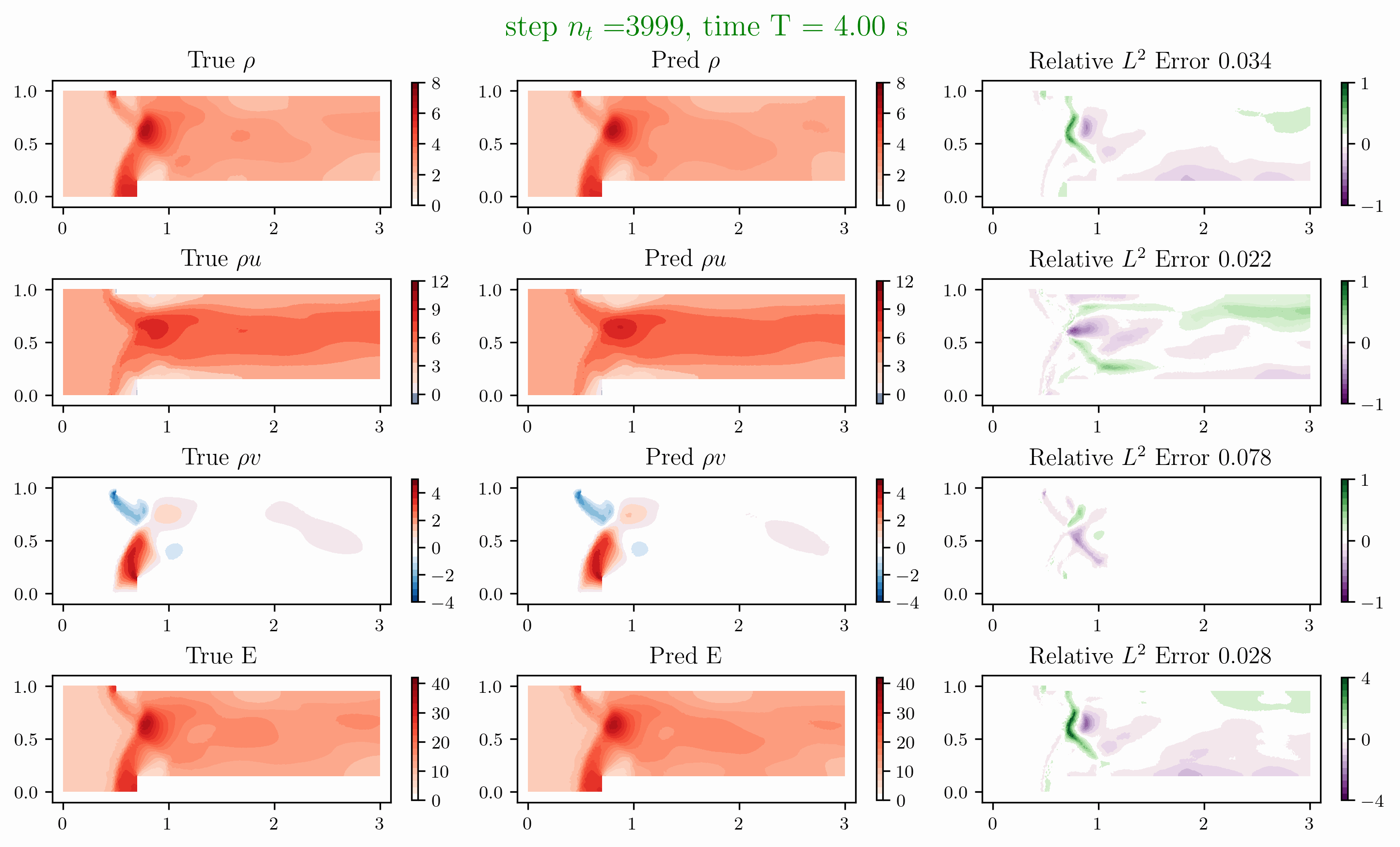
Problem 5. ScramJet
- Training data is generated from Model 1 with time interval [0,1.6]s
- Test data is generated from Model 1 and Model 2 for time interval [0, 6]s
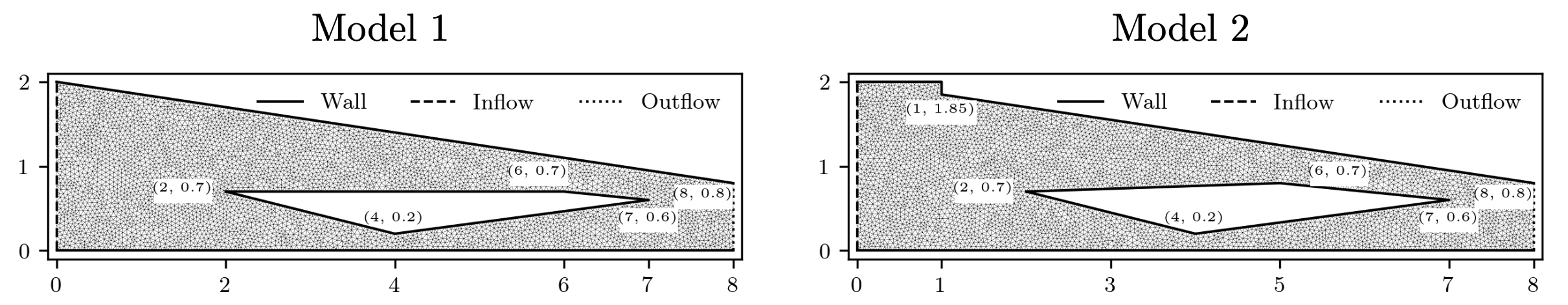
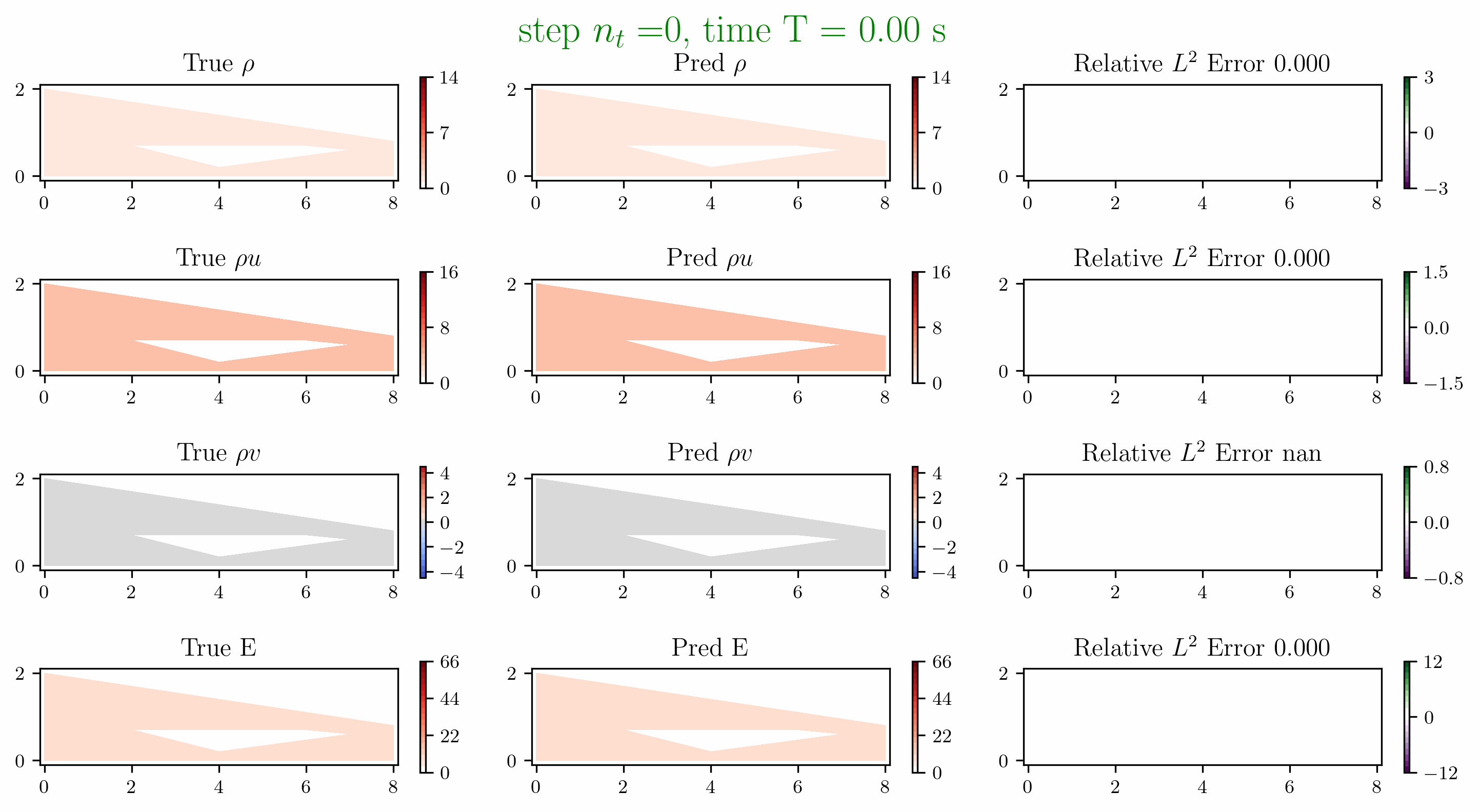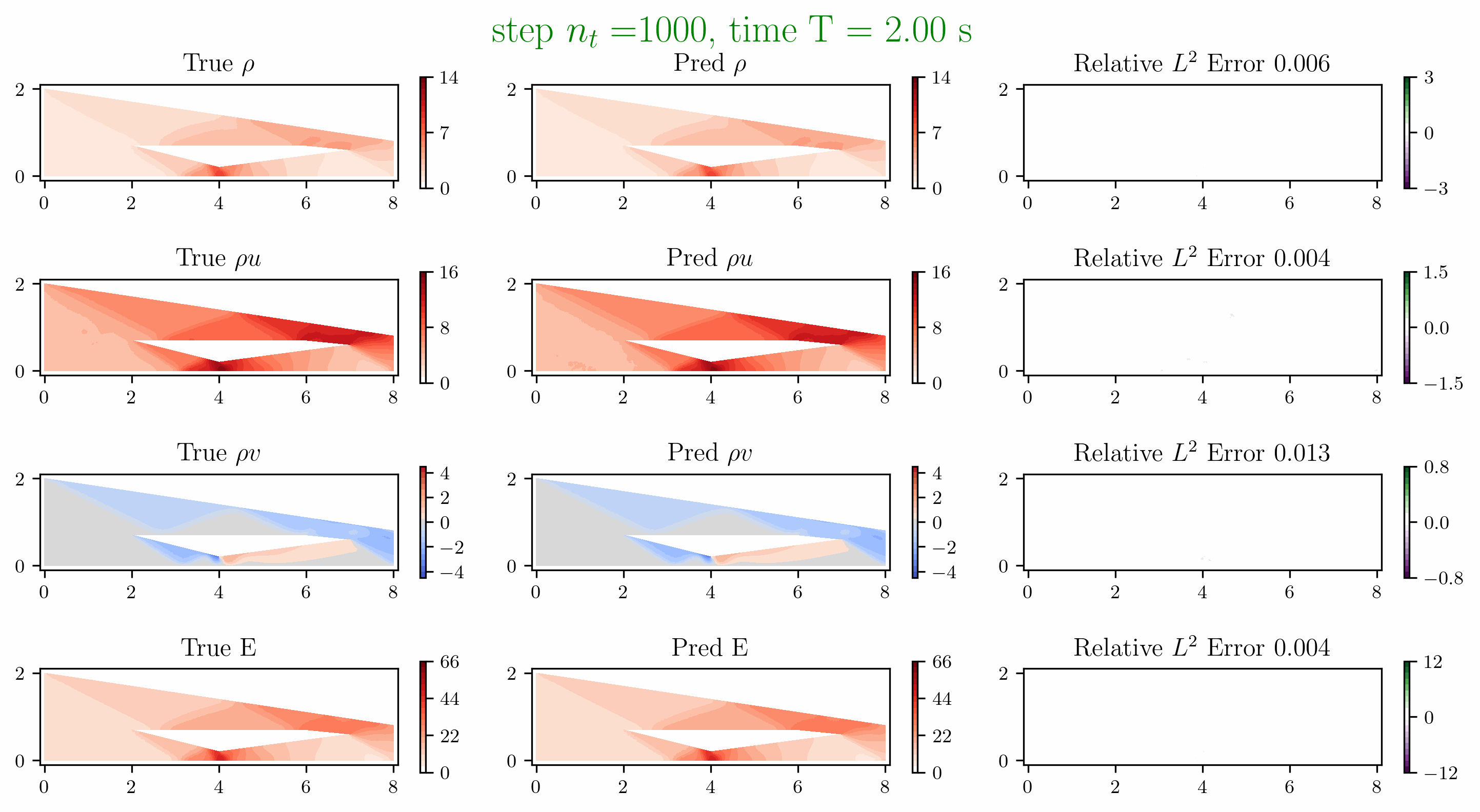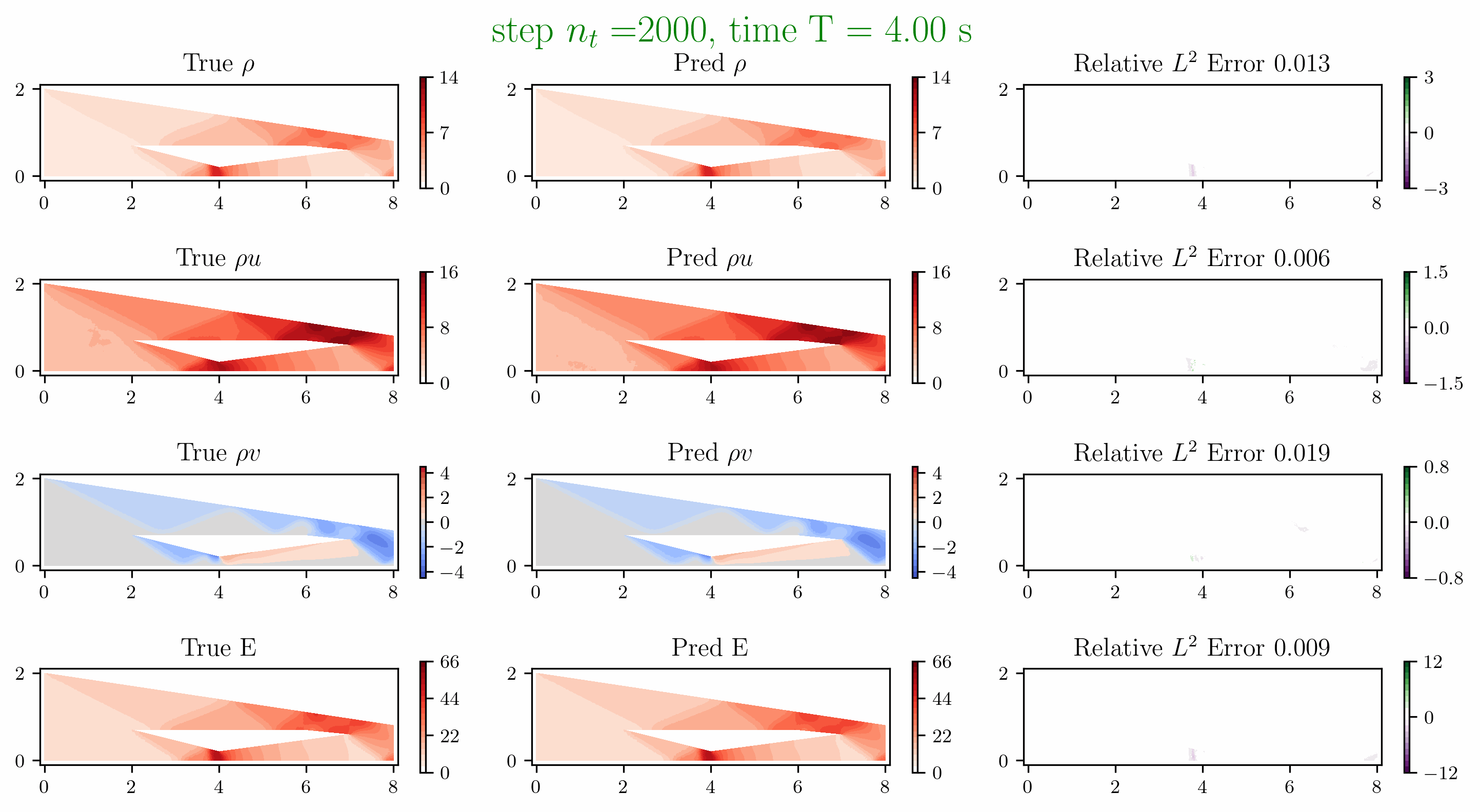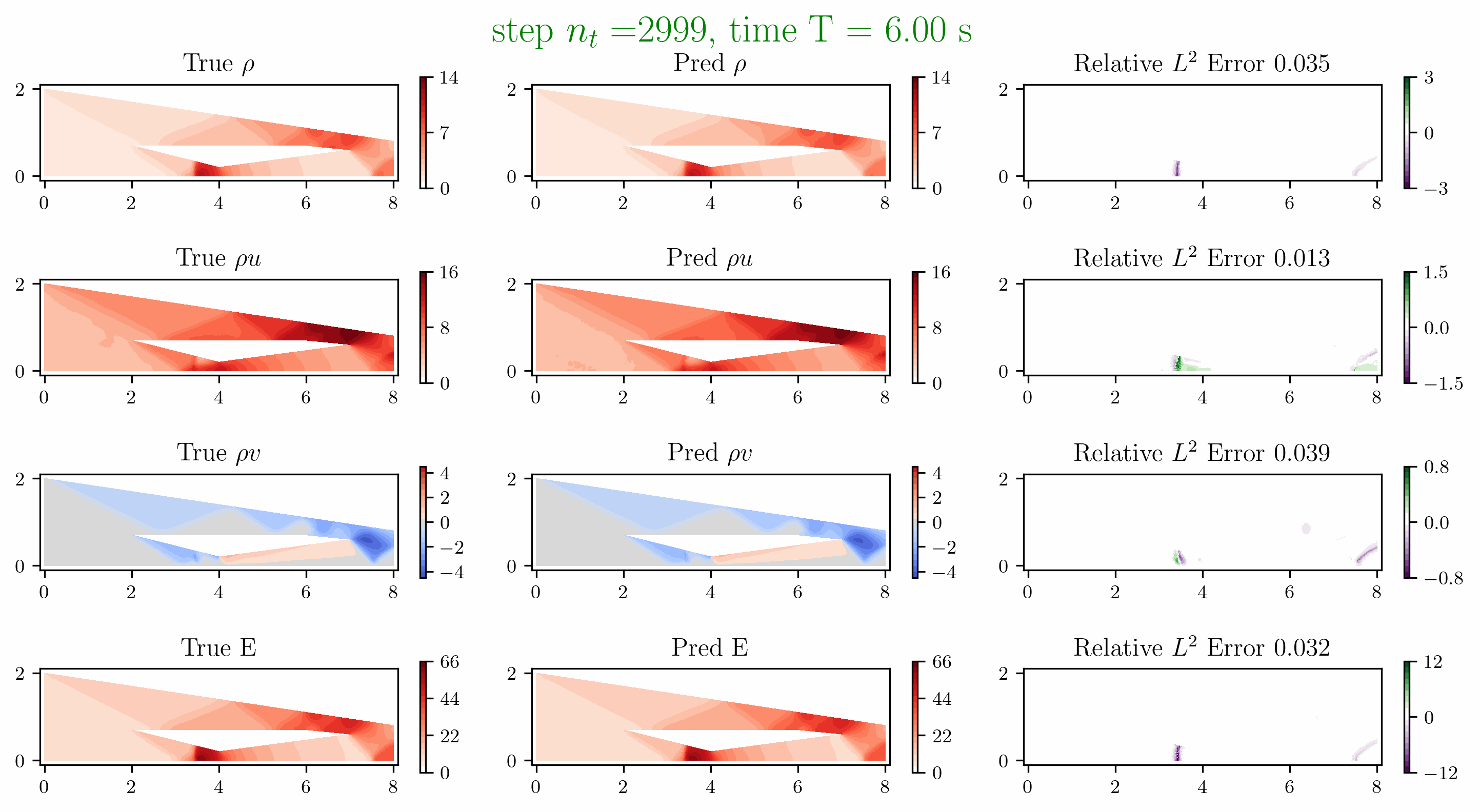
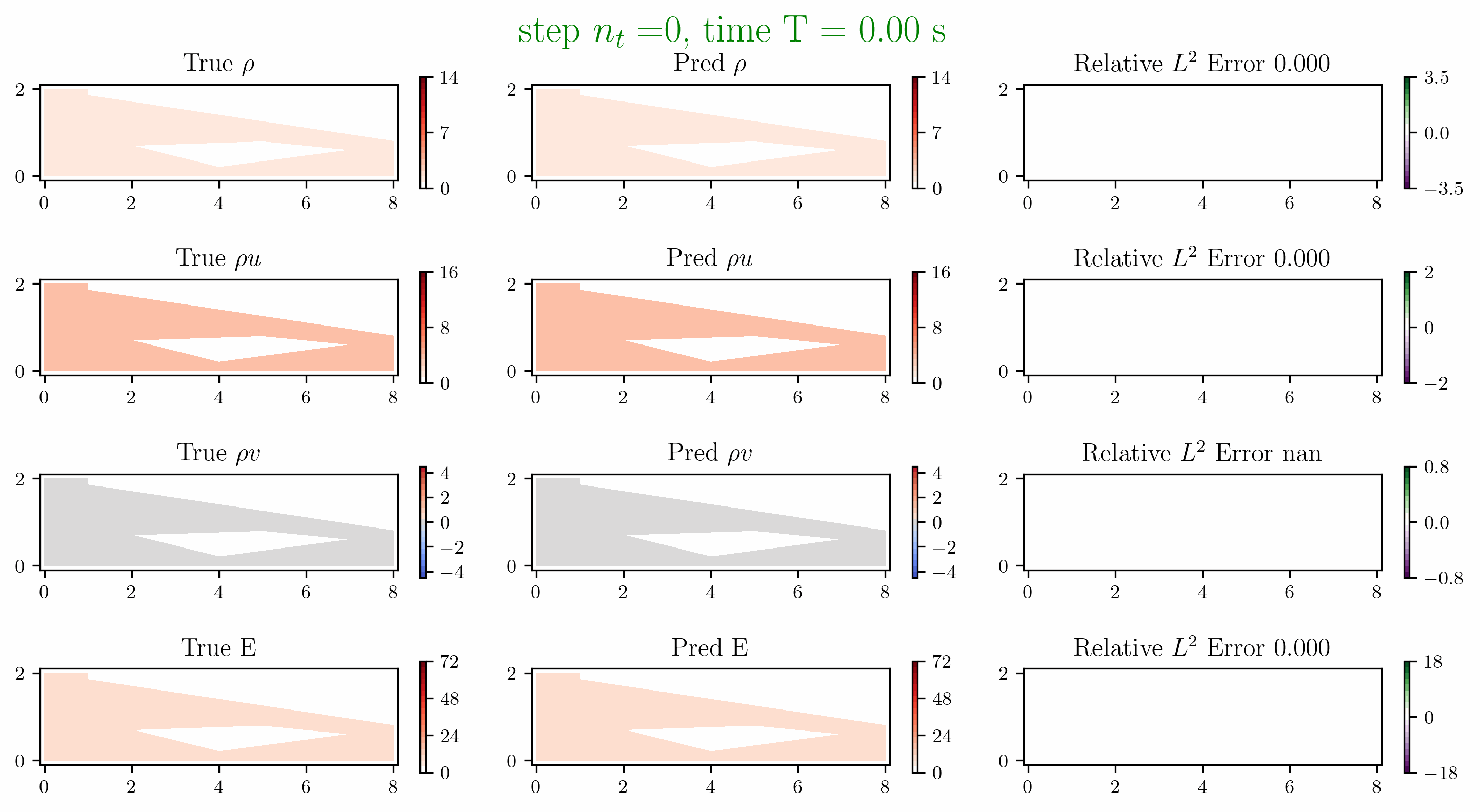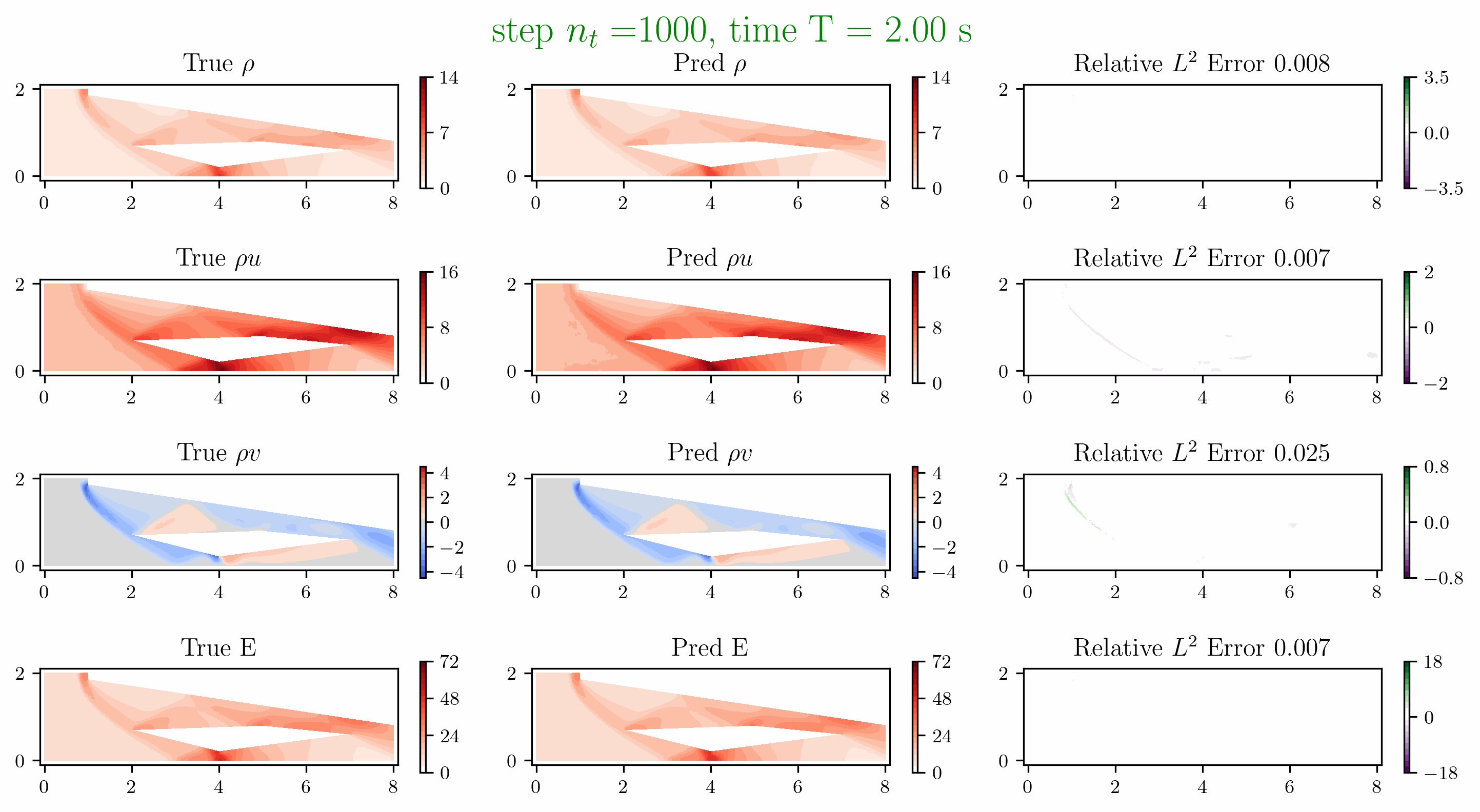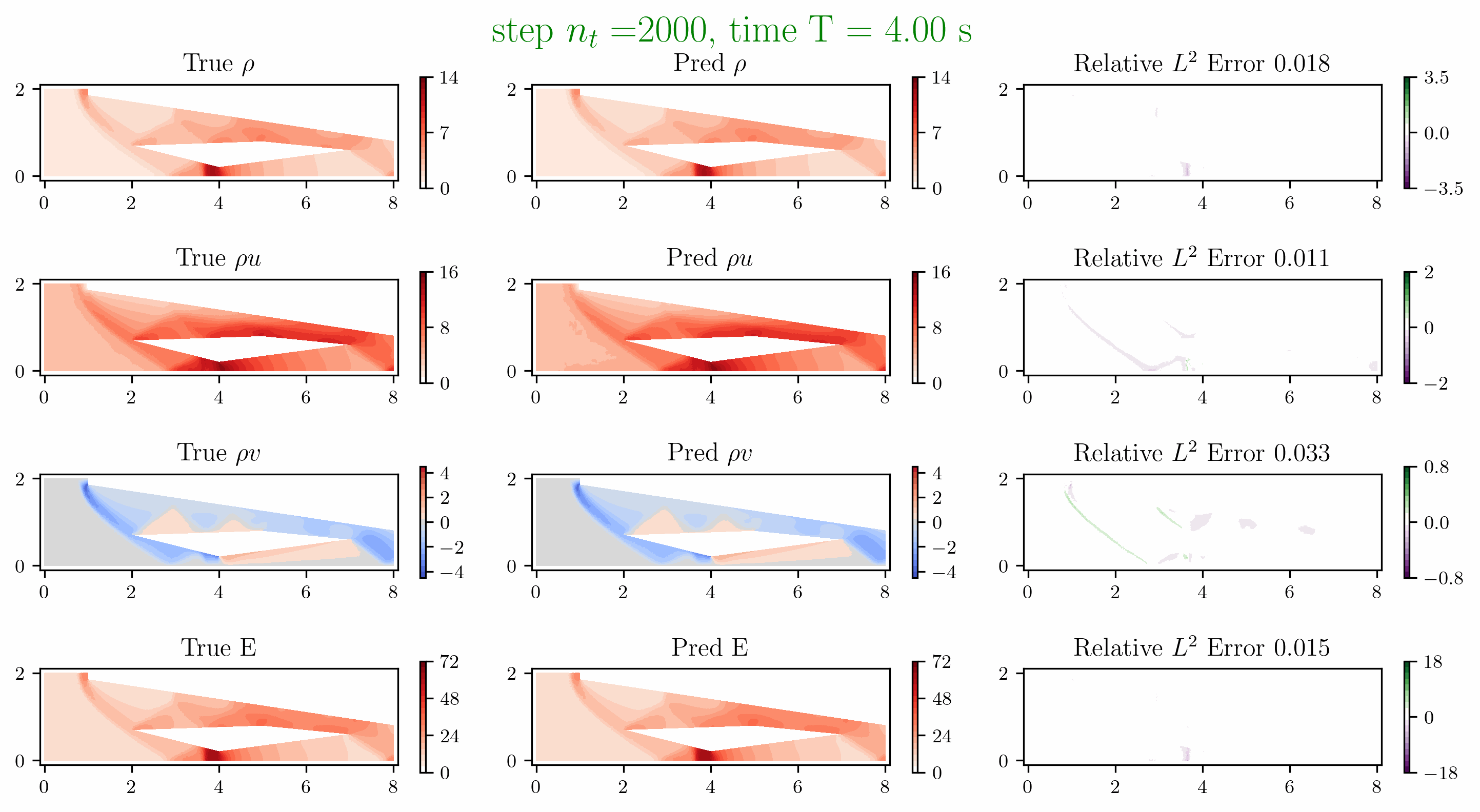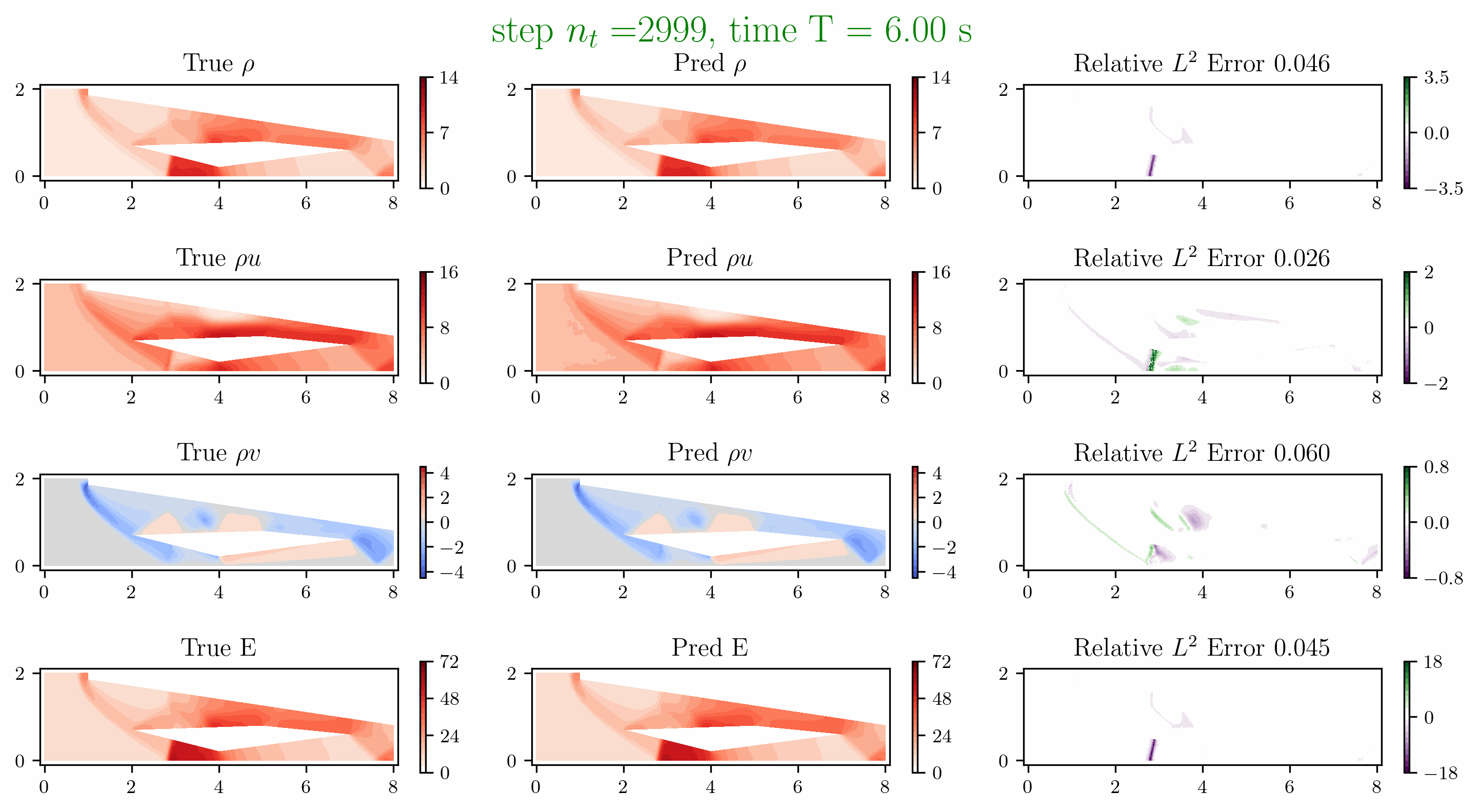
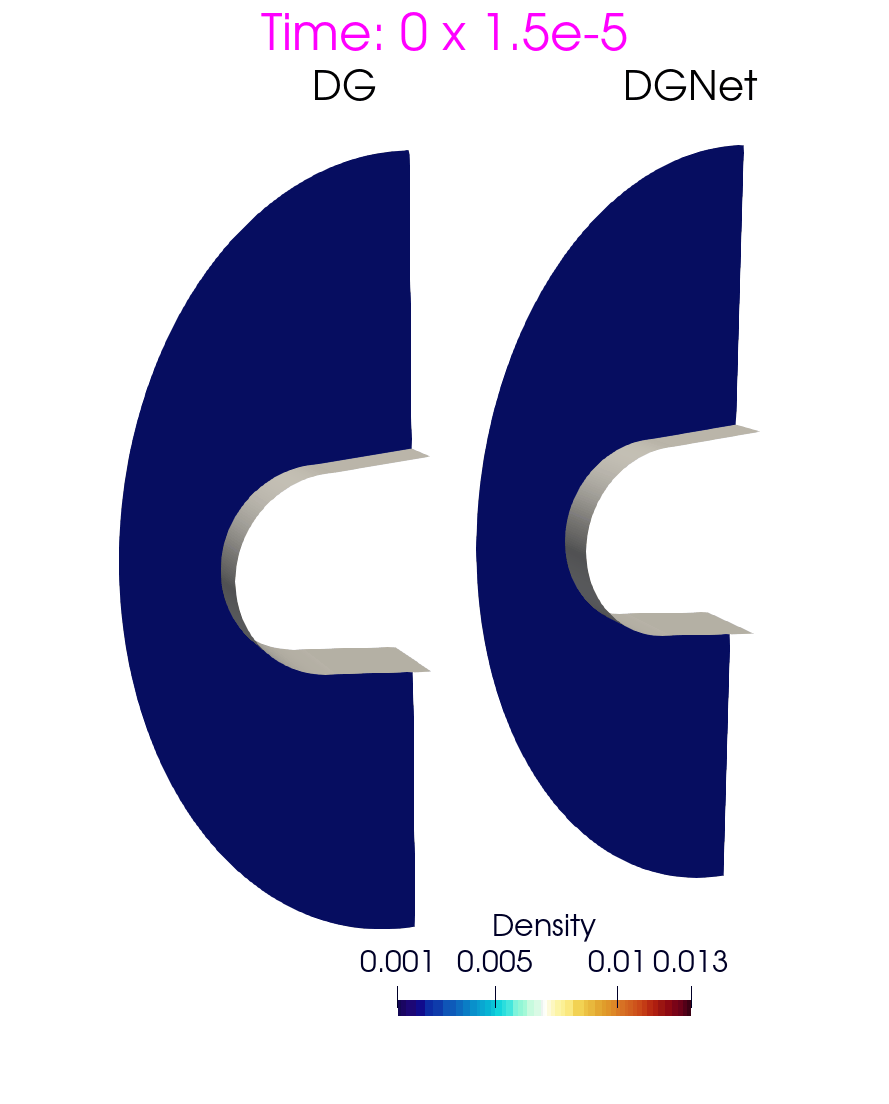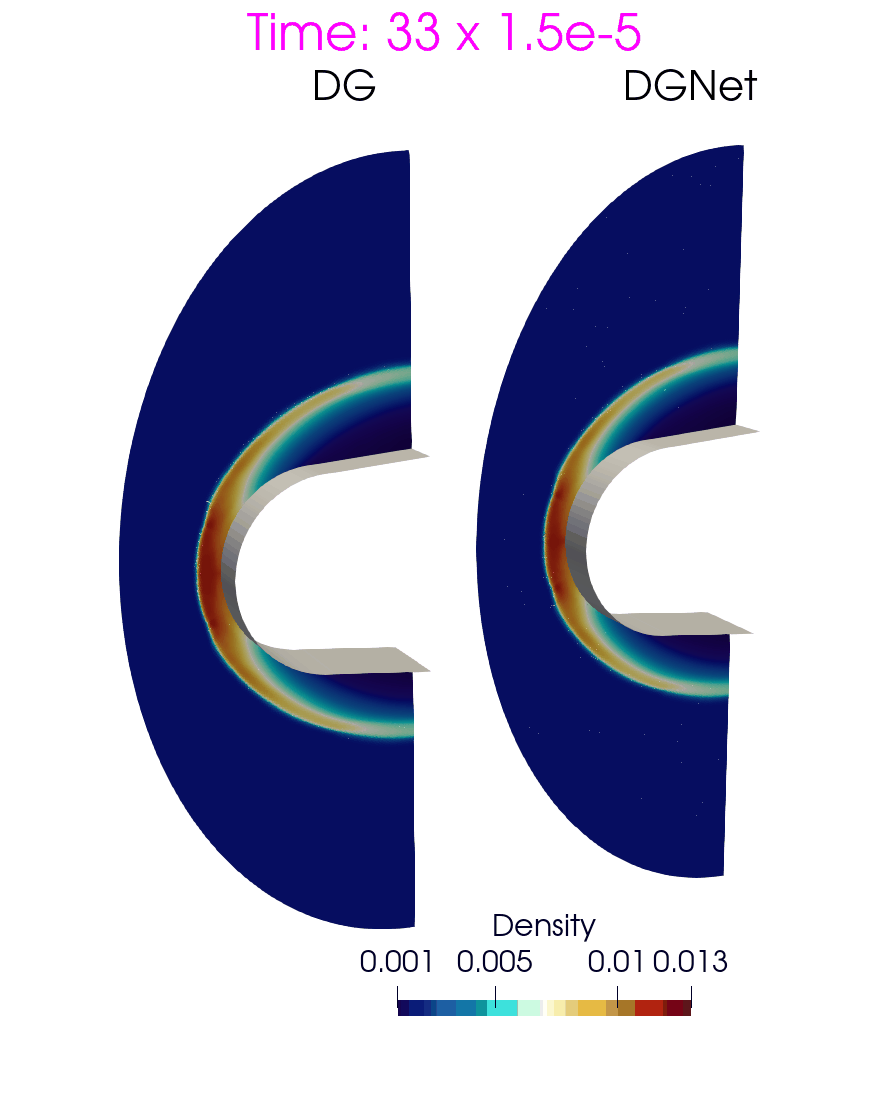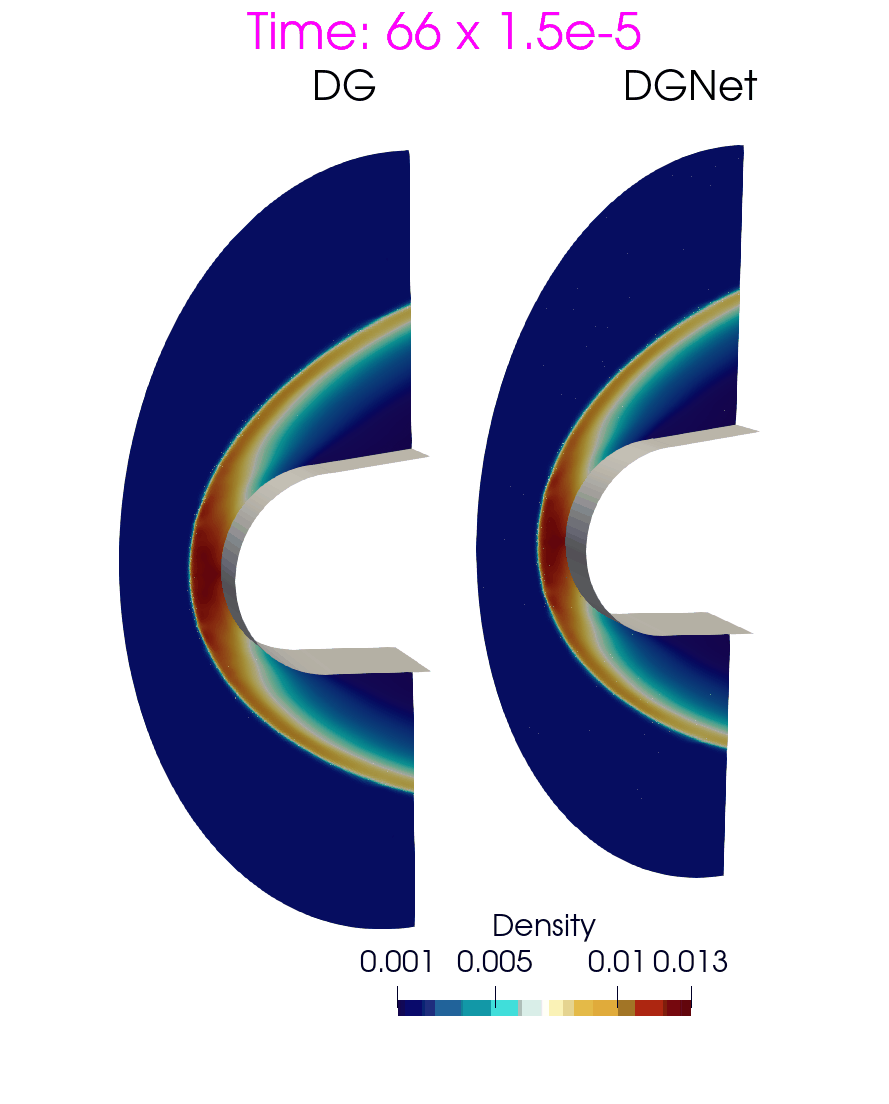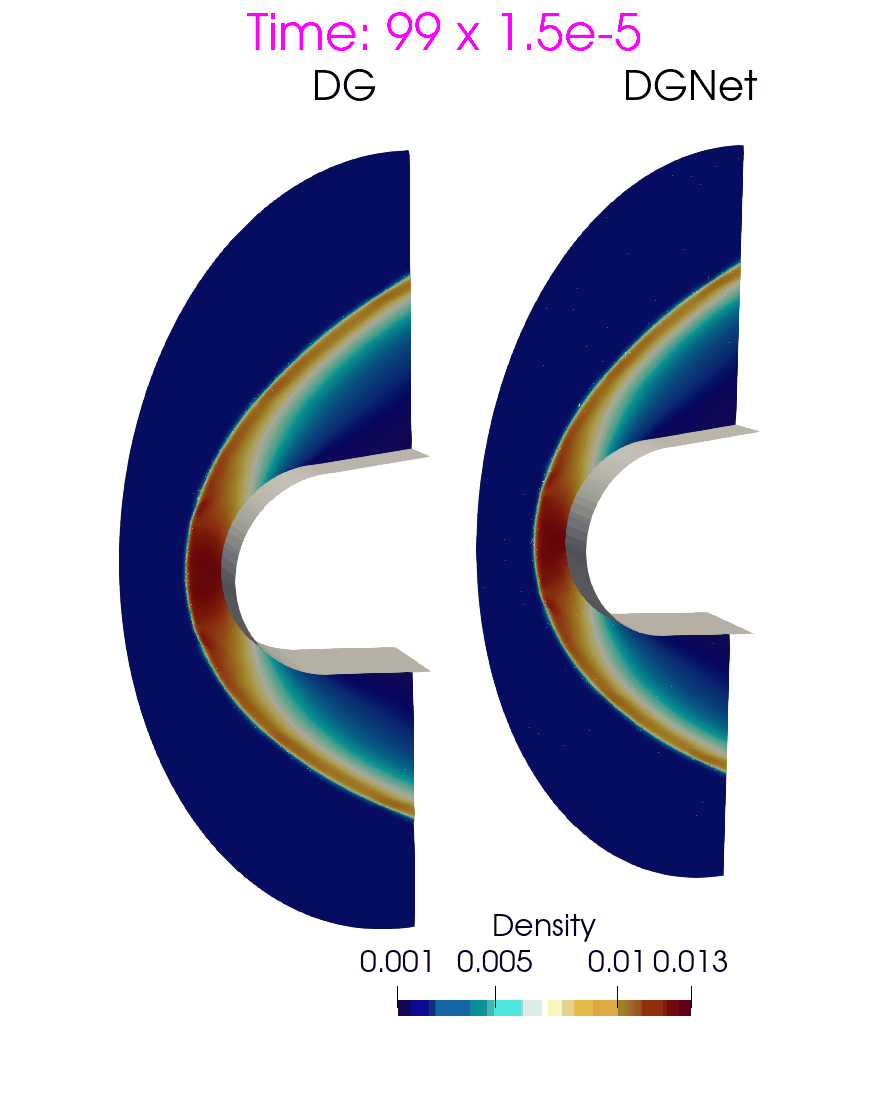
Problem 6. Hypersonic flow over a sphere cone
- Training data is generated with time interval [0,3e-4]s
- Test data is generated with time interval [0, 1.5e-3]s