Deep-learning enhanced model reduction method
Major Activities
This project focus on forecasting solution of time-dependent PDE’s based on the Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) method. The idea is to approximate the PDE solution \(u(t,x)\) as a linear combination of orthonormal modes (SVD of the snapshot matrix):
\[u(t,x)=\sum_{j=1}^r U_j \alpha_j(t)\]A neural network is then used to fit the time-dependent coefficients (\(\alpha_r(t):\) \(r\) dimensional output) at different time instants (\(1\) dimensional inputs). However, this approach can only predict solution within the training data set and fails at forecasting the solution accurately at a future time instant (i.e outside the training data set). In order to deal with this issue, we haved develoepd a model-constrained approach to take the underlying mathematical model into account.
Significant Results
For demonstration, we consider the linear advection equation driven by an external force. A time-varying boundary condition is adopted and only the first two dominant modes are considered in approximating the solution. The forecasted solution is shown below. It is clear that one can forecast the solution accurately at a future time instant by encoding the mathematical models into the learning process.
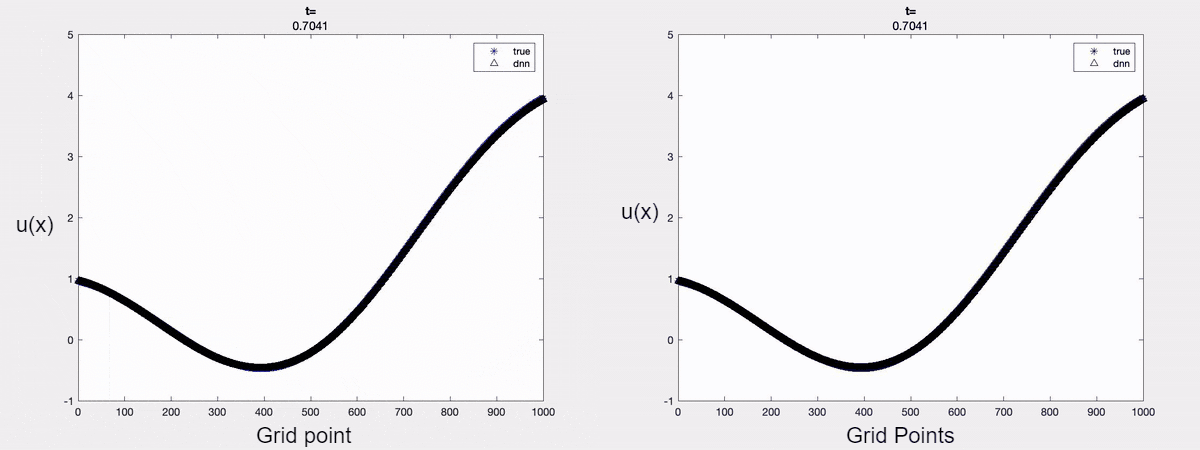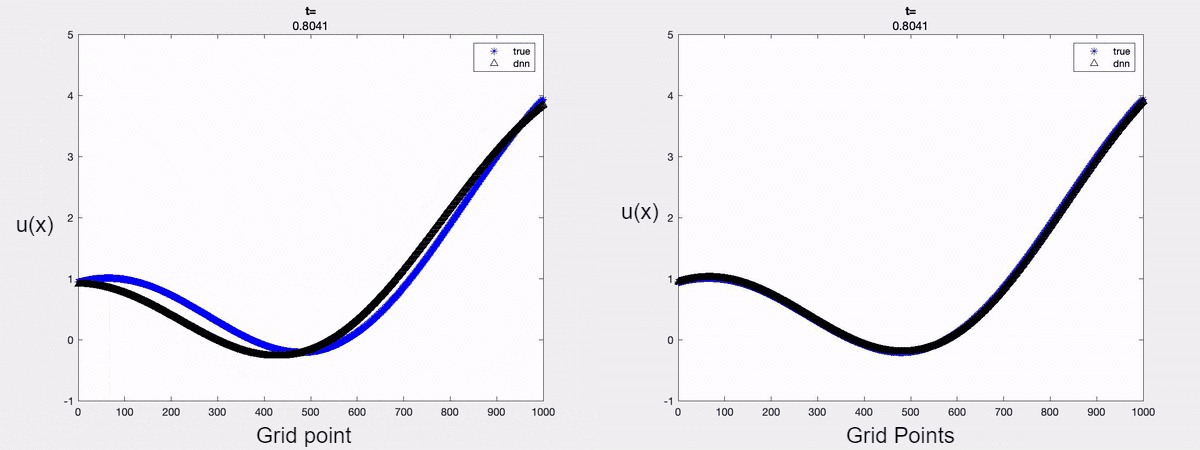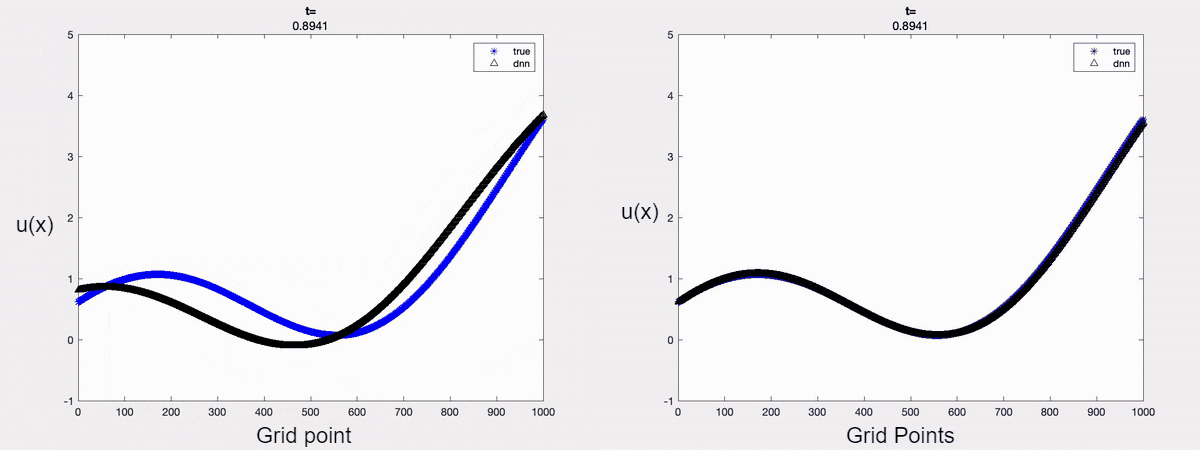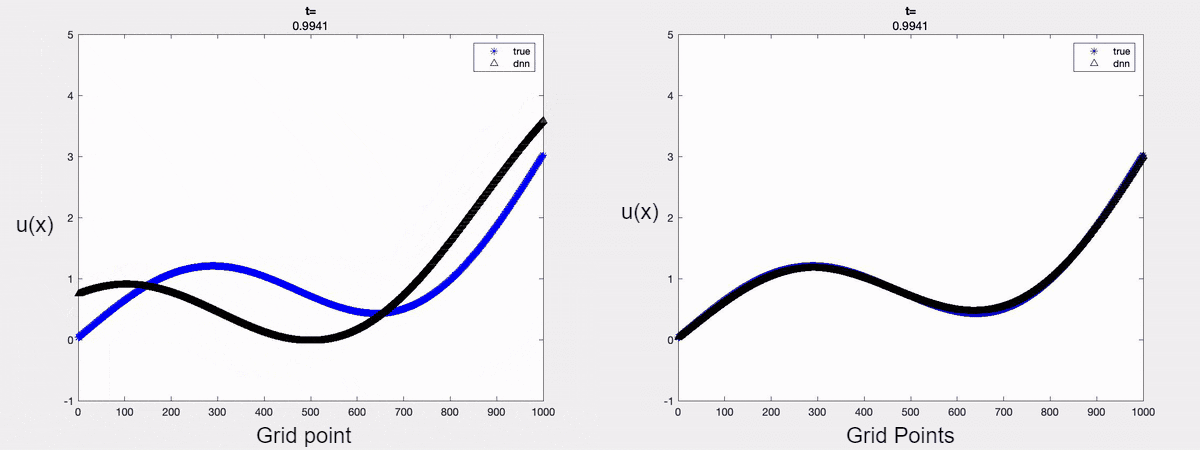
Fig 1: a) Forecasted solution without the Physics constraint (on the left);
b) Forecasted solution with the Physics constraint (on the right)